* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chromomere - aqinfo.com
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
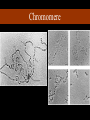
Chromomere Bead like projections – along entire length of polytene chromosome Heavier stained than inter-chromomeric regions Clear in dipteran salivary gland chromosome as dark bands Genes are located within chromomere One chromomere – single gene Evidence – local coiling of continuous DNA thread Chromomere Chromomere Vary in size Chromomere next to centromere – larger and progressively smaller towards chromosome ends Number is constant – polytene chromosome Serve as reliable morphological characteristic Telomere Two ends of chromosomes – end caps of chromosomes Highly stable and don’t fuse or unit with telomers of other chromosomes If telomeres are damaged/removed – end are highly unstable and fuse with broken ends of other chromosomes – resulting in translocations or ring chromosomes Structural identity and individuality of chromosome is maintained due to telomeres Telomeres – enlarged terminal chromomeres Sometimes show centromeric activity - neocentromere Telomere Two distinct regions Protelomeres: terminal deep staining structure with sharp limits, three large chromomeres Eutelomere: weakly staining sub-terminal region adjacent to protelomeres One compound telomere – eight chromomeres Irregular folded chromatin fibres loop back into chromatid Telomere Prevent shortening of chromosomes during cell division Made up of both DNA and proteins Sequence motif ‘TTAGGG’ is highly conserved Retrotelomeres: composed of large number of terminal repeats, clustered around chromosome ends