Effete, a Drosophila chromatin-associated ubiquitin
... 2011). In most organisms, telomeres terminate with tandemly repeated of G-rich sequences, which are added to chromosome ends by the telomerase holoenzyme (Blackburn et al. 2006). These telomere short repeats associate with sequence-specific binding factors, which in turn recruit additional telomeric ...
... 2011). In most organisms, telomeres terminate with tandemly repeated of G-rich sequences, which are added to chromosome ends by the telomerase holoenzyme (Blackburn et al. 2006). These telomere short repeats associate with sequence-specific binding factors, which in turn recruit additional telomeric ...
New elements in modern biological theories of aging
... and other repair mechanisms cannot correct defects as fast as they are apparently produced. In particular, there is evidence for DNA damage accumulation in non-dividing cells of mammals. Genetic mutations occur and accumulate with increasing age, causing cells to deteriorate and malfunction. Damage ...
... and other repair mechanisms cannot correct defects as fast as they are apparently produced. In particular, there is evidence for DNA damage accumulation in non-dividing cells of mammals. Genetic mutations occur and accumulate with increasing age, causing cells to deteriorate and malfunction. Damage ...
Chemistry and biology of DNA-binding small
... sequence selectivity and affinity. Inhibition by transcription can either result from competition with transcriptionfactor binding or from physical arrest of the RNA polymerase. For activation of the transcription, the TFOs should be covalently linked to an activation domain. ...
... sequence selectivity and affinity. Inhibition by transcription can either result from competition with transcriptionfactor binding or from physical arrest of the RNA polymerase. For activation of the transcription, the TFOs should be covalently linked to an activation domain. ...
An RNA transcriptional regulator templates its own regulatory RNA
... that mapped to the location of the primary cleavage site identified by the hydroxyl radical proximity experiment. These results provide the first evidence that E. coli RNAP can use a biologically important RNA as a substrate for site-specific RNA synthesis. The authors next assessed the consequence ...
... that mapped to the location of the primary cleavage site identified by the hydroxyl radical proximity experiment. These results provide the first evidence that E. coli RNAP can use a biologically important RNA as a substrate for site-specific RNA synthesis. The authors next assessed the consequence ...
Telomereled bouquet formation facilitates homologous chromosome
... and several cosmid DNAs as probes for unique sequences on chromosome II (see Figure 1). Three other probes were also used: YIp10.4 for rRNA gene clusters (rDNA) located at both termini of chromosome III, cos212 for telomeres of chromosomes I and II, and pRS140 for the centromeres of all chromosomes. ...
... and several cosmid DNAs as probes for unique sequences on chromosome II (see Figure 1). Three other probes were also used: YIp10.4 for rRNA gene clusters (rDNA) located at both termini of chromosome III, cos212 for telomeres of chromosomes I and II, and pRS140 for the centromeres of all chromosomes. ...
Chaperone-like activity of the AAAş proteins Rvb1 and
... cells [54,55,61]. This mechanism is essential in a range of cellular processes, such as transcriptional regulation, chromosome segregation, cell cycle progression and DNA damage response. The catalytic subunit of the complex is the Swr1/ SRCAP protein, which is an SNF2 helicase. Rvb1, Rvb2, Act1, Ar ...
... cells [54,55,61]. This mechanism is essential in a range of cellular processes, such as transcriptional regulation, chromosome segregation, cell cycle progression and DNA damage response. The catalytic subunit of the complex is the Swr1/ SRCAP protein, which is an SNF2 helicase. Rvb1, Rvb2, Act1, Ar ...
Replication and Recombinantion
... the fact that nucleotide bases contain nitrogen Thus DNA contains nitrogen The most common form of nitrogen is N14 with 7 protons and 7 neutrons N15 is called “heavy nitrogen” as it has 8 neutrons thus increasing its mass by 1 atomic mass unit ...
... the fact that nucleotide bases contain nitrogen Thus DNA contains nitrogen The most common form of nitrogen is N14 with 7 protons and 7 neutrons N15 is called “heavy nitrogen” as it has 8 neutrons thus increasing its mass by 1 atomic mass unit ...
Epigenetic mechanisms regulate placental c-myc
... proliferation. Overexpression of c-myc resulting in the up-regulation of many other genes is known to be involved in the development of cancer. The catalytic subunit of hTERT is one such c-myc downstream target gene (Horikawa et al., 1999). C-myc overexpression thus has a role in telomerase activati ...
... proliferation. Overexpression of c-myc resulting in the up-regulation of many other genes is known to be involved in the development of cancer. The catalytic subunit of hTERT is one such c-myc downstream target gene (Horikawa et al., 1999). C-myc overexpression thus has a role in telomerase activati ...
CHROMOSOMES
... The X and Y chromosomes are known as the sex chromosomes because of their crucial role in sex determination. The X chromosome was originally labeled as such because of uncertainty as to its function when it was realized that in some insects this chromosome is present in some gametes but not in other ...
... The X and Y chromosomes are known as the sex chromosomes because of their crucial role in sex determination. The X chromosome was originally labeled as such because of uncertainty as to its function when it was realized that in some insects this chromosome is present in some gametes but not in other ...
Cockayne Syndrome group B protein interacts
... patients carrying CSB mutations may be defective in telomere maintenance. INTRODUCTION Telomeres are heterochromatic structures found at the ends of linear eukaryotic chromosomes. Mammalian telomeric DNA consists of tandem repeats of TTAGGG that are bound by a telomere-specific complex known as ...
... patients carrying CSB mutations may be defective in telomere maintenance. INTRODUCTION Telomeres are heterochromatic structures found at the ends of linear eukaryotic chromosomes. Mammalian telomeric DNA consists of tandem repeats of TTAGGG that are bound by a telomere-specific complex known as ...
The Epigenetics Behind Human Aging
... of these free radicals increases. Furthermore, the Hayflick limit is another piece of the aging picture. Human cells can only replicate so many times; with each division, the telomeres associated with a cell’s DNA will shorten and eventually reach a point where they are too short to continue divisio ...
... of these free radicals increases. Furthermore, the Hayflick limit is another piece of the aging picture. Human cells can only replicate so many times; with each division, the telomeres associated with a cell’s DNA will shorten and eventually reach a point where they are too short to continue divisio ...
Journal of Clinical Oncology
... characteristic value of 0.94.3 This series is the largest reported, both in number of cases and controls. This report also has the best sensitivity and specificity for detecting cases among all the series reported. Using a different method of assessing hTERT DNA, Chen et al6 reported elevated levels ...
... characteristic value of 0.94.3 This series is the largest reported, both in number of cases and controls. This report also has the best sensitivity and specificity for detecting cases among all the series reported. Using a different method of assessing hTERT DNA, Chen et al6 reported elevated levels ...
Identification of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Genes Whose Deletion
... cells have abnormal vacuolar morphology (Michaillat and Mayer 2013). SKT5 encodes a protein that activates the chitin synthetase Chs3 that helps form spore walls (Iwamoto et al. 2005). skt5D cells have decreased vegetative growth rate and decreased viability (Kozubowski et al. 2003; Byrne and Wolfe ...
... cells have abnormal vacuolar morphology (Michaillat and Mayer 2013). SKT5 encodes a protein that activates the chitin synthetase Chs3 that helps form spore walls (Iwamoto et al. 2005). skt5D cells have decreased vegetative growth rate and decreased viability (Kozubowski et al. 2003; Byrne and Wolfe ...
Full Text
... † ADE2–ADE3 -based reporter system for plasmid-loss assay (as shown in Figure 1A). R, solid red colonies; S, sectored colonies. ‡ URA3 -based reporter system for plasmid-loss assay. Y, grew on 5-FOA; N, no growth on 5-FOA; Y/N, a fraction of the cells grew on 5-FOA. § Complementation tests using cdc ...
... † ADE2–ADE3 -based reporter system for plasmid-loss assay (as shown in Figure 1A). R, solid red colonies; S, sectored colonies. ‡ URA3 -based reporter system for plasmid-loss assay. Y, grew on 5-FOA; N, no growth on 5-FOA; Y/N, a fraction of the cells grew on 5-FOA. § Complementation tests using cdc ...
National Human Genome Research Institute
... copied and distributed in the vast majority of cell divisions. Still, mistakes do occur on rare occasions. ...
... copied and distributed in the vast majority of cell divisions. Still, mistakes do occur on rare occasions. ...
Homologous Recombination Generates T-Loop
... (Marciniak et al., 2000; Mitchell et al., 1999; Vulliamy et al., 2001). Here, we document that HR can delete large segments of telomeric DNA in human and mouse cells and suggest that this pathway has implications for telomere-related disease states. Telomeres protect chromosome ends from inappropria ...
... (Marciniak et al., 2000; Mitchell et al., 1999; Vulliamy et al., 2001). Here, we document that HR can delete large segments of telomeric DNA in human and mouse cells and suggest that this pathway has implications for telomere-related disease states. Telomeres protect chromosome ends from inappropria ...
COMMENTARY Hypothesis on the Role of Cytoplasmic “Short Base
... Because of its cunning characteristic, there are always a mass of cancer cells in the body when cancer is detected. So it is very difficult to find the first cancer cells. In the new theory, we focus on the formation of the first cancer cells which also called the cancer- stem cells. We classify the ...
... Because of its cunning characteristic, there are always a mass of cancer cells in the body when cancer is detected. So it is very difficult to find the first cancer cells. In the new theory, we focus on the formation of the first cancer cells which also called the cancer- stem cells. We classify the ...
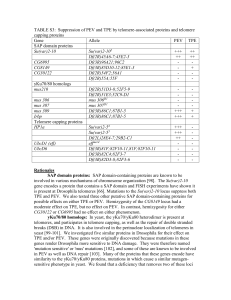
TABLE S3: Suppression of PEV and TPE by telomere
... gene encodes a protein that contains a SAP domain and FISH experiments have shown it is present at Drosophila telomeres [66]. Mutations to the Su(var)2-10 locus suppress both TPE and PEV. We also tested three other putative SAP domain-containing proteins for possible effects on either TPE or PEV. He ...
... gene encodes a protein that contains a SAP domain and FISH experiments have shown it is present at Drosophila telomeres [66]. Mutations to the Su(var)2-10 locus suppress both TPE and PEV. We also tested three other putative SAP domain-containing proteins for possible effects on either TPE or PEV. He ...
SCIENCE AS A PROCESS
... Then grow in 14N, centrifuge as generations divide, and check to see where heavy DNA ends up ...
... Then grow in 14N, centrifuge as generations divide, and check to see where heavy DNA ends up ...
Tudor – Down`s syndrome
... mean that they would get slowly eroded over time. Instead, telomeres effectively “cap” chromosomes in a way that allows for removal of nucleotides at the ends of the chromosome during replication, without endangering vital coding sequences (Blackburn 2009). Because of this vital role, telomeric ...
... mean that they would get slowly eroded over time. Instead, telomeres effectively “cap” chromosomes in a way that allows for removal of nucleotides at the ends of the chromosome during replication, without endangering vital coding sequences (Blackburn 2009). Because of this vital role, telomeric ...
Chapter 5 Gases - Saint Demetrios Astoria School
... • Mice genetically engineered to have no telomerase enzymes age prematurely – Life expectancy declines by about half ...
... • Mice genetically engineered to have no telomerase enzymes age prematurely – Life expectancy declines by about half ...
Telomere maintenance without telomerase
... telomeres of a telomerase-pro®cient strain. However, these elongated telomeres still exhibited the same gradual shortening observed during the initial senescence of a newly generated telomerase-defective strain, suggesting that the recombination mechanism that was replenishing telomeric repeats was ...
... telomeres of a telomerase-pro®cient strain. However, these elongated telomeres still exhibited the same gradual shortening observed during the initial senescence of a newly generated telomerase-defective strain, suggesting that the recombination mechanism that was replenishing telomeric repeats was ...
DNA and genetic information
... Information in binary computers • two basic symbols :1 or 0 (“bits”) • physical form of bits varies with medium • 8 bit words = bytes (e.g 10110111) • 28 = 256 unique bytes are possible • This is a large enough set of symbols to represent characters in language ...
... Information in binary computers • two basic symbols :1 or 0 (“bits”) • physical form of bits varies with medium • 8 bit words = bytes (e.g 10110111) • 28 = 256 unique bytes are possible • This is a large enough set of symbols to represent characters in language ...
Telomerase

Telomerase also called telomere terminal transferase is a ribonucleoprotein that adds the nucleotide ""TTAGGG"" to the 3' end of telomeres, which are found at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes. A telomere is a region of repetitive sequences at each end of a chromatid, which protects the end of the chromosome from deterioration or from fusion with neighbouring chromosomes.Telomerase is a reverse transcriptase enzyme that carries its own RNA molecule (with the pattern of ""CCCAAUCCC"" in vertebrates), which is used as a template when it elongates telomeres.