* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chp 2 Cell structure
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
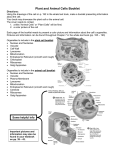
What is cell? Cell is the basic unit that build up organism. What do you call the structures in a cell? The structures in a cell is called organelles. State the organelles in an animal cells. Cell membrane, mitochondrion, rough endoplasmic reticulum, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, ribosome, centriole, golgi apparatus. Animal Cell 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Plant Cell ch cw Plant Cell Chloroplast Cytoplasm Nucleus Vacuole Cell membrane Cell wall (made of cellulose) Nucleus Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosome Golgi Apparatus Plasma membrane Mitochondrion Lysosome Centrioles Chloroplast Cell Wall Activity 2.1.2 Draw a table to list the functions of organelles in animal cells and plant cells. Organelles Functions Task 2.1.2 Complete the below table to state the functions of each organelle. Organelle Functions Cell membrane Cell membrane forms a boundary to separate the content of a cell from outer environment. Cell membrane regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cytoplasm. Cell wall Cell wall gives shape to a plant cell. Cell wall provides mechanical support for the plant cells. Cytoplasm Cytoplasm acts as a medium for biochemical reactions in the cell. Nucleus Nucleus contains genetic information that determines the characteristics and functions of the cell. Nucleus controls all the activities which take place in the cell. vacuole Vacuole regulates water balance in the cell. Vacuole acts as a storage place in a cell. Mitochondrion Mitochondria carry out cellular respiration to release energy in form of ATP. Ribosome Ribosomes synthesise protein. Endoplasmic reticulum Rough ER transports proteins made by ribosome. Smooth ER is the site of metabolic reactions – synthesis of lipids and detoxification of drugs and poisons. Golgi apparatus Golgi apparatus process, package and transport carbohydrates, proteins, phospholipid and glycoprotein. Lysosome Lysosome contains hydrolytic enzymes to digest complex organic molecules. Lysosome eliminates worn out mitochondria and other damaged organelles. Centriole Centriole functions during cell division in animal cells. Chloroplasts Chloroplast traps sunlight and converts light energy into chemical energy during photosynthesis You have learnt about the cellular components of animal and plant cells. Now, carry out a discussion among your group to compare and contrast the structure of animal and plant cells. You can present your findings by using table. Animal Cell Plant Cell Animal Cell CORRECTIONS Plant Cell Animal cell does not have fixed Plant cell has fixed/regular shape. Similarities: shape / regular shape. Both animal cell and plant cell have a Animal cell does not have cell Plant cell has cell wall. nucleus, a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, wall. Golgi rough Animal cellapparatus, does not have mitochondria, All green plants have chloroplasts. endoplasmic reticulum,chloroplasts. smooth endoplasmic Animal cell does not have Mature plant cell has a large reticulum and ribosomes. vacuole or if have, vacuoles are central vacuole. usually small and numerous. Differences: Animal cell has centrioles. Plant cell does not have centrioles. Animal cell stores carbohydrate in Plant cell stores carbohydrate in the form of glycogen. the form of starch. How does a unicellular organism perform its living processes? •It depends on its cellular components which include the organelles. The density of organelles in specific cells Multicellular organisms are made up of many types of cells. The cells undergo specialisation to become specific in order to perform different function. Therefore, certain organelles are found abundantly in the specific cells. For example, pancreatic cells which synthesise and secrete enzymes and hormones contain a high density of rough endoplasmic reticulum. Cells Tissues Organism Organs Systems Example of cell organisation in digestive system in a human Cell organisation Cell organisation in mammals Cells Tissues Organs Systems Permanent tissues Meristematic tissues are Young, actively Dividing cells haven’t have Differention are have consist of Tips of roots and buds of shoots Mature tissues Differention located at thin walls, large nuclei, dense cytoplasm, no vacuoles. Organism epidermal tissues, ground tissues, vascular tissues. Different types of cells in plants which have been undergone specialisation Plant cell types in tissues – Ground tissues Parenchyma • “typical” plant cells = least specialized • photosynthetic cells, storage cells • tissue of leaves, stem, fruit, storage roots Collenchyma • unevenly thickened primary walls = support Sclerenchyma •very thick, “woody” secondary walls = support •rigid cells that can’t elongate • dead at functional maturity Vascular tissue •Transports materials in roots, stems & leaves Xylem •-carry water & minerals up from roots •tube-shaped dead cells •only their walls provide a system of microscopic water pipes Phloem •carry nutrients throughout plant •sugars (sucrose), amino acids… • tube-shaped living cells Regulating the internal environment Cells bathe in the internal environment which contain interstitial fluid. The internal environment must be regulated to maintain its level. Do you know why? The constant internal environment ensure the cells to function optimally. The process involves in maintaining the balance of homeostasis internal environment is called …………………………. Which type of mechanisms involves in homeostatic mechanism? The value rises above the set point Normal value (set point) Corrective mechanism Normal value (set point) The value drops below the set point Corrective mechanism Vacuole Sample Answer : Compare and contrast animal cell and plant cell Animal Cell Plant Cell •Both animal cell and plant cell have plasma membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus and mitochondrion. •Animal cell has centriole and •Plant cell does not have centriole lysosome. and lysosome. •Animal cell does not have cell wall, large central vacuole, and chloroplast. •Animal cell has irregular shape. •Animal cell stores carbohydrates in the form of glycogen. •Plant cell has cell, wall, large central vacuole, and chloroplast. •Plant cell has regular / fixed shape. •Plant cell stores carbohydrates in the form of starch. Sample Answer: By giving appropriate examples, describe how different organelles work together to enable the cell to function in an orderly manner. Pancreas cell functions to produce enzyme. To produce enzyme, ribosome sends mRNA messenger to nucleus to copy DNA code. mRNA messenger returns to ribosome. Ribosome synthesise proteins based on the code. Proteins enters rough endoplasmic reticulum and is enclosed in vesicle. Vesicle with proteins fuses with Golgi apparatus. The proteins is modified to form specific enzyme. Then, the enzyme is enclosed in secretory vesicle. The secretory vesicle will fuse with plasma membrane and releases the enzyme out from the cell.