* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Vacuole
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
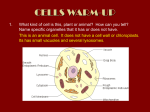
Cell biology Vacuole The vacuole can occupy between 20 and 90% of a cell’s volume. Vacuole It contains mostly water with dissolved inorganic and organic substances. The vacuole is surrounded by a semipermeable membrane called the tonoplast. Back to main anatomy menu Next Back to cell biology menu Main menu Cell biology Vacuole In meristematic cells or specialized cells like the guard cells in a stomate, there are numerous small vacuoles (red stars) in the cell. * * * * Back to main anatomy menu Back Next * * * Back to cell biology menu Main menu Cell biology Vacuole In a mature parenchyma cell, the vacuole occupies most of the cell and pushes the cytoplasm and organelles to the periphery of the cell. A major function of the vacuole is maintaining cellular turgor by regulating water movement within the cell. Vacuole Chloroplasts Electron micrograph of a parenchyma cell. Back to main anatomy menu Back Next Back to cell biology menu Main menu Cell biology Vacuole The vacuole regulates the turgor pressure in a cell by actively moving ions (especially potassium) across the tonoplast membrane. Turgor is created by moving water by osmosis into the vacuole exerting more pressure against the cell wall. Guard cells In the guard cells of a stomate, the stomatal aperture is open when the cell has reduced turgor pressure and is closed when cells are fully turgid. Back to main anatomy menu Back Next Back to cell biology menu Main menu Cell biology Vacuole The vacuole may store reserve materials such as proteins, sugars and organic acids or they can accumulate various compounds like tannins and anthocyanins. The vacuole can also be involved with cellular waste management, enzymatically digesting or storing unwanted substances. Anthocyanin Tannins Vinca (Catharanthus) petal Back to main anatomy menu Back Pine (Pinus) leaf Next Back to cell biology menu Main menu Cell biology Vacuole In specialize storage cells like those in some seeds, protein is stored in membrane-bound protein bodies that form from the vacuole. Protein bodies in legume cotyledon cells. Back to main anatomy menu Back Next Back to cell biology menu Main menu Cell biology Vacuole Various types of crystals can also form within the vacuole. Crystals Raphide crystals Back to main anatomy menu Back Back to cell biology menu Main menu