* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MEASUREMENT OF CELL COUNT AND VIABILITY
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
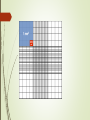
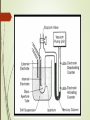
CELL COUNTING AIM OF CELL COUNTING = to determine growth in cultures. DIRECT METHODS INDIRECT METHODS HEMOCYTOMETER PROTEIN AND DNA ESTIMATION ELECTRONIC CELL COUNTER GLUCOSE UPTAKE HEMOCYTOMETER Thick glass plate fits into stage of microscope . most common type is Neubauer cytometer. grooved calibrated grid consist of 9 large squares with Imm side each. square further sub divided into 25 squares which is further subdivided into 16 squares of 0.05mm side. cell suspension is put into the hemocytometer and viewed under microscope. Each cell contain 0.1 µl of cell suspension. Cell per ml = total count/ 5 x 10-4 Cell viability check by using TRYPAN BLUE DYE which permeates into non-viable cells. mixture of citric acid and crystal violet causes cell to lysis and the released nuclei stains purple. used for viability measurement. % of viability = no. of viable cells total cell count x 100 ADVANTAGES simple and effective. DISADVANTAGES Expected error is 10%. Laborious method . If many samples being analysed. ELECTRONIC CELL COUNTER Electronic device which is suitable for cell counting rapidly. 0.5ml of cell suspension is diluted in PBS (phosphate buffer saline) and is pass through a small pore of 70µ in diameter. Cell cause measureable change in electrical resistance as they passed between 2 electrodes. One inside and one outside the glass tube. Pulses are recorded by oscilloscope. resistance produce is directly proportional to the volume of the cells. The expected error is 5%. ADVANTAGES High speed for counting large no. of samples. Expected error is less than 5%. Particles smaller than cell can be eliminated from the count by setting lower threshold of detection. DISADVANTAGES Cell aggregates should not present in sample otherwise cell count will underestimated. Cell suspension above (10)4 per ml should be diluted otherwise two or more cell passing through counting zone at the same time will causes error.