* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Surface/Intercell Communication Division
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
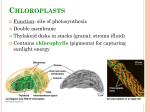
Cell Surface/Intercell Communication Division By Clint Lockwood, Jacob Hanson & Jaelyn Richter Flagella, Cilia, and Cell Movement Flagella: A lash-like appendage that protrudes from the cell body of certain prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Cilia: A slender protuberance organelle that projects from a much larger cell body. Cell Movement: 1. Response to an external signal in its surrounding environment a. can be a physical, chemical, diffusible or non-diffusible signal that is detected by receptor proteins i. First, a cell propels the membrane forward by orienting and growing the actin network at its leading edge. ii. Second, it adheres to the substrate at the leading edge and releases at the cell body and rear of the cell. iii. Finally, contractile forces, pull the cell forward Cell Walls Cell Wall: A rigid layer outside the plasma membrane of the cells of plants, fungi, and bacteria. ● Turgor pressure: pushes the plasma membrane against the walls of these cells o o o Healthy plants are turgid Activates enzymes that allow for the cell wall to grow and expand Rely on turgidity to maintain rigidity o Limited plasticity/rigidity prevents the cell from rupturing, provides protection, allows for cellular expansion ● Glue to bind neighboring cells together ● Determines mechanical/tensile strength ● Barrier to prevent other cells from getting to the cell membrane ● Contributes to cellular communication Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Definition: A substance that contains collagen, elastin, proteoglycans, glycosaminoglycans, and fluid that is produced by cells and in which the cells are embedded. ● Secreted by chondroblasts which is responsible for the properties of forming cartilage. ● Osteoblasts for bone Functions: Mechanical support for cells Segregates tissues from one another Regulates intercellular communication Embryonic development Importance: For growth, wound healing, and fibrosis Plasmodesmata Plasmodesmata: microscopic channels which traverse the cell walls of plant cells and some algal, enabling transport and communication. 1. Enables direct, regulated, simplistic transport of substances between cells. 2. There are two forms of plasmodesmata: primary plasmodesmata, which are formed during cell division, and secondary plasmodesmata, which can form between mature cells. 3. Transport of… a. Messenger RNA b. Proteins c. Viral Genomes d. Short Interfering RNA Plasma Membrane Cell Wall Callose Endoplasmic Reticulum Desmotubule Adhering Junctions Adherens junctions: protein complexes that occur at cell–cell junctions in epithelial and endothelial tissues, usually more basal than tight junctions 1. A cell junction whose cytoplasmic face is linked to the actin cytoskeleton 1. The accepted model has been that adherens junctions serve as a bridge connecting the actin cytoskeleton of neighboring cells through direct interaction Works Cited http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/extracellular+matrix http://biology.kenyon.edu/edwards/project/greg/pd.htm http://users.rcn.com/jkimball.ma.ultranet/BiologyPages/J/Junctions.html http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flagellum http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plasmodesma http://pixshark.com/flagella-cell-structure.htm http://www.nature.com/nrm/journal/v10/n1/fig_tab/nrm2597_F2.html http://www.lookfordiagnosis.com/mesh_info.php?term=Extracellular+Matrix&lang=1 http://themedicalbiochemistrypage.org/glycans.php http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pulmonary-fibrosis/basics/definition/con-20029091 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK21047/ http://uwf.edu/jgould/Importance%20of%20Intercell%20Comm%20p1.pdf http://toxsci.oxfordjournals.org/content/68/2/265.full http://www.uta.edu/biology/wilk/classnotes/cellphys/extracellular%20matrix.pdf http://study.com/academy/lesson/extracellular-matrix-function-components-definition.html http://users.rcn.com/jkimball.ma.ultranet/BiologyPages/E/ECM.html