* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
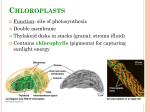
Notes Ch. 6 part 2 Mitochondrion • site of cellular respiration • enclosed by 2 membranes: outer is smooth & inner is convoluted (cristae) • between membranes is intermembrane space • interior is called the matrix • contains its own DNA & ribosomes • number in cell is related to cell’s level of metabolic activity Chloroplast • site of photosynthesis • contains chlorophyll • found in leaf cells & cells of other green organs • enclosed by 2 membranes with a narrow intermembrane space • interior fluid is called the stroma • stroma contains stacks of membranous sacs called thylakoids (a stack of thylakoids is called a granum) • contains its own DNA & ribosomes Peroxisome • bound by a single layer of phospholipids • contains enzymes that catalyze oxidation reactions producing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) as a by-product • additional enzymes break down the H2O2 which is toxic to the cell Cytoskeleton • network of fibers extending throughout cytoplasm • provides mechanical support to the cell • maintains the shape of the cell • anchors organelles • involved in cell movement (cilia & flagella) • may also be involved in the regulation of biochemical activities Components of the Cytoskeleton • microtubules – shape & support the cell – serve as tracks for the movement of organelles – separate chromosomes during cell division – “9+2” arrangement and dynein arms cause cilia & flagella to beat – grow out from centrosome (which includes a pair of centrioles in animal cells) continued • microfilaments (actin filaments) – built from molecules of actin – help cell bear tension (pulling forces) – play a role in cell motility – works with myosin to cause muscle cell contraction in animals & cytoplasmic streaming in plant cells • intermediate filaments – help cell bear tension – reinforces shape of cell – helps anchor organelles – make up nuclear lamina (lining on nuclear side of nuclear envelope) Cell Wall • protects & maintains shape of plant cell • prevents excessive uptake of water • composed primarily of cellulose in plants & chitin in fungi • perforated by channels called plasmodesmata that connect adjacent cells Extracellular Matrix • consists primarily of glycoproteins (carbohydrate attachments to membrane proteins) • most abundant glycoprotein is collagen Intercellular Junctions • Plant Cells – plasmodesmata = cytoplasmic channels between adjacent plant cells • Animal Cells – tight junctions = bind cells tightly together to prevent fluid from leaking into surrounding tissues – desmosomes = anchoring junctions (fasten cells together) – gap junctions = cytoplasmic channels between adjacent animal cells