* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Specialised Cells
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
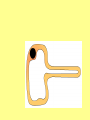
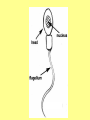
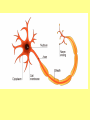
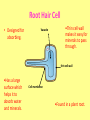
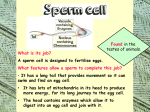
Specialised Cells Lesson 1 1. Identify one similarity and one difference in the structure of plant and animal cells: Similarity: __________________________________________ __________________________________________ Difference: __________________________________________ __________________________________________ 2 marks [Total 2 marks] Specialised Cells Learning outcomes • Be able to name some specialised cells • Describe the jobs of some specialised cells • Describe how specialised cells are adapted for their jobs On MWB name the cell Specialised Cells • Plants and animals are multicellular (consist of many cells). • They contain many different types of cells. • Each type of cell is designed to carry out a particular job or function. • This is known as CELL SPECIALISM • Not all cells look the same. • Some cells have a special shape and features to help them do a certain job. Sperm cell Head nucleus Designed to Fertilise eggs. Found in the Testes Tail A sperm is small and has a long tail that provides movement so it can swim and find an egg cell. The head contains enzymes which allow it to digest into an egg cell and join with it. Egg (Ovum) Cell • Designed to be Fertilised. Cytoplasm containing yolk • Found in the Ovaries. • An egg cell is large and bulky. Layer of jelly Nucleus • Contains yolk which provides a large food store for the new cell being formed. Palisade Cell • Designed for Photosynthesis Nucleus • Found in the top of a leaf • Tall and has a large surface area to absorb water and minerals. • Packed with chloroplasts to help make plant food. Chloroplasts Root Hair Cell • Designed for absorbing. Vacuole •Thin cell wall makes it easy for minerals to pass through. thin cell wall •Has a large surface which helps it to absorb water and minerals. Cell membrane •Found in a plant root. Nerve Cell (neurone) Nucleus •They are long •They have connections at each end •Can carry electrical signals •Their job is to carry nerve impulses to different parts of the body. Red Blood Cell •Designed to carry oxygen •Found in blood. •Large surface area, for oxygen to pass through. •Contains haemoglobin, which joins with oxygen. •Has no nucleus Model Cell 1. Decide which cell you know the least about. 2. Make a model cell using coloured paper. 3. Make sure you add as many labels as possible. Peer assessment 1. Look at the model cell of the person next to you. – Have they included the job of the cell? – Have they included the adaptations of the cell? 2. Write them a www and an ebi