* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download i. Genetics
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
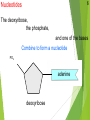
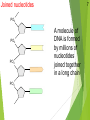
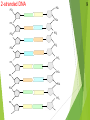
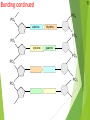
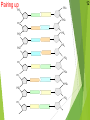
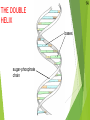
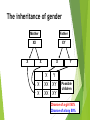
Genetics New Learning Goal: To describe how genetics are passed from one generation to another. Fun Facts…. 1. Monkeys and Humans have 98.8%of the same DNA. 2. Humans have 50% of the same DNA as bananas. 3. You get 99.9% of your DNA from your parents. Let’s let my buddy, Bill Nye introduce us to Genetics…. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OZIQTMHmWmg Gregor Mendel (1822-1884) The Father of Genetics copyright cmassengale 5 Gregor Johann Mendel Austrian monk Studied the inheritance of traits in pea plants Developed the laws of inheritance Mendel's work was not recognized until the turn of the 20th century 6 Gregor Johann Mendel Between 1856 and 1863, Mendel cultivated and tested thousands of pea plants He found that the plants' offspring retained traits of the parents copyright cmassengale 7 Particulate Inheritance Mendel stated that physical traits are inherited as “particles” Mendel did not know that the “particles” were actually Chromosomes & DNA copyright cmassengale 8 I. What is genetics? i. Genetics The study of _______ (how traits are passed from parents to offspring) I. What is genetics? i. Genetics The study of heredity (how traits are passed from parents to offspring) ii. Heredity How an organism passes ____ from one generation to the next. ii. Heredity How an organism passes traits from one generation to the next. iii. Trait A __________ or quality of an organism iii. Trait A characteristic or quality of an organism v. Variability The differences between ________ in a given population v. Variability The differences between organisms in a given population vi. Adaptation A structure or behavior that allows an organism to survive in its environment. sidewinder article Exit Ticket 1. Who is the father of Genetics? 2. What is heredity? 3. What is a trait? 4. Describe adaptation that we saw with the snakes. 1 New Learning Goal: To describe how genetics are passed from one generation to another. BrainPop Time…. http://www.brainpop.com/health/geneticsgrowtha nddevelopment/dna/ DNA DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid This chemical substance is present in the nucleus of all cells in all living organisms The kind of cell which is formed, (muscle, blood, nerve etc.) is controlled by DNA The kind of organism which is produced (giraffe, herring, human, etc.) is controlled by DNA 2 Ribose & deoxyribose Ribose is a sugar, like glucose, but with only five Oxygen atoms in its molecule Deoxyribose is almost the same but lacks one oxygen atom Both molecules may be represented by the symbol 4 5 The bases The most common organic bases are Adenine Thymine Cytosine Guanine (A) (T) (C) (G) 6 Nucleotides The deoxyribose, the phosphate, and one of the bases Combine to form a nucleotide PO4 adenine deoxyribose Joined nucleotides 7 PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 A molecule of DNA is formed by millions of nucleotides joined together in a long chain 8 In fact, the DNA usually consists of a double strand of nucleotides The sugar-phosphate chains are on the outside and the strands are held together by chemical bonds between the bases 2-stranded DNA PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 9 10 Bonding The bases always pair up in the same way Adenine forms a bond with Thymine Adenine Thymine and Cytosine bonds with Guanine Cytosine Guanine Bonding continued 11 PO4 PO4 adenine thymine PO4 PO4 cytosine guanine PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 Pairing up PO4 12 PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 PO4 13 The paired strands are coiled into a spiral called A DOUBLE HELIX 14 THE DOUBLE HELIX bases sugar-phosphate chain 15 A model of part of a DNA molecule Build a DNA molecule – you try it! Your Exit Tickets will be Passed Out Now CHROMOSOMES New Learning Goal: To describe how genetics are passed from one generation to another. Numbers of chromosomes Constant for each cell in the body. Constant throughout the life of an individual (you don’t lose or gain chromosomes) Constant species © 2007 Paul Billiet ODWS for all members of a Organism Human Chromosome numbers 46 Chimpanzee 48 House Mouse 40 Maize 20 © 2007 Paul Billiet ODWS Human chromosomes Identifying chromosomes Chromosomes can be identified by: Their size Their shape and flexiblity Banding patterns Chromosomes are analyzed by organising them into a KARYOTYPE © 2007 Paul Billiet ODWS Female Male The inheritance of gender Mother Father XX XY X X X X Y X XX XY X XX XY Y Possible children Chance of a girl 50% Chance of a boy 50% Exit Ticket: On the back of your notes, create a Punnett Square for Blue Eyes and Brown Eyes. Dominant and Recessive Traits New Learning Goal: To describe how genetics are passed from one generation to another. Before we begin, let’s take a look at a quick video…. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Mehz7tCxjSE What are traits? Physical Traits Can be seen by others Eye color, hair color, height, left handed Acquired Traits Learned skills Playing a sport, riding a bike, playing a musical instrument Behavioral Traits Instinctual Nest actions building and migration Terms Used in Modern Genetics Genotype The particular alleles (genes) an individual carries They are inherited from your biological parents Genes control your traits Phenotype An individual’s observable traits What people can SEE when they look at you Terms Used in Modern Genetics An individual with non-identical alleles of a gene is heterozygous for that gene Examples: Two or more alternative forms of a gene. Bb, Tt, Aa An individual with identical alleles of a gene is homozygous for that gene Examples: BB or bb, TT or tt Terms Used in Modern Genetics An allele is dominant if its effect masks the effect of a recessive allele paired with it Capital letters (A) signify dominant alleles; lowercase letters (a) signify recessive alleles Homozygous dominant (AA) Homozygous recessive (aa) Heterozygous (Aa) What traits do you have? We will go through the most common traits that people have On your sheet, record if you have the mentioned trait or not You may have to ask your neighbor for help Detached (EE, Ee) or attached (ee) Earlobes Can Tongue Roll (TT, Tt) or Can’t (tt) Dimples (DD, Dd) No Dimples (dd) Right (RR, Rr) or Left (rr) handed? Freckles (FF, Ff) No Freckles (ff) Curly (HH, Hh) or Straight (hh) Cleft Chin (CC, Cc) or No Cleft (cc) Allergies (AA, Aa) or No Allergies (aa) Normal (BB, Bb) Color Blindness (bb) Can you see the number inside the circle? If you cannot, you may be colorblind Widow’s Peak (WW, Ww) or Straight (ww) Data Please compare your results (the chart) with 5 other students. Does our data support which genes are dominant and which genes are recessive?