* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Prof. Kamakaka`s Lecture 12 Notes
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
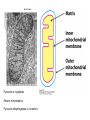
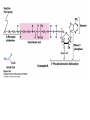
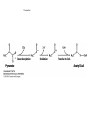
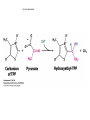
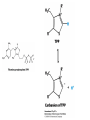
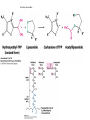
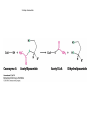
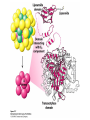
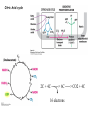
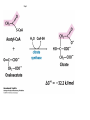
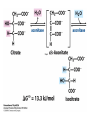
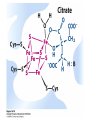
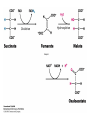
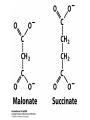
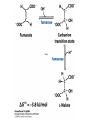
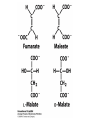
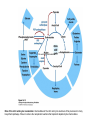
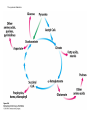
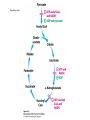
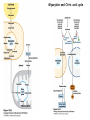
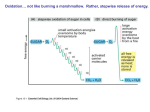
The Citric Acid cycle Pyruvate to Acetyl CoA Pyruvate and acetyl-CoA used for energy AND to synthesize amino acids and lipids etc Mitochondria Pyruvate in cytoplasm Enters mitochondria Pyruvate dehydrogenase is in matrix Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Huge complex (50nm) (ribosome is 5nm) Three sub-complexes- E1, E2 and E3 Commits pyruvate to AcCoA formation Pyruvate dehydrogenase Pyruvate to Acetyl CoA The reaction Ist step intermediate 2nd step intermediate 3rd step intermediate 4th step Reactions in the complex Co-ordinated substrate channeling-pass substrate form 1 active site to next Fast reaction, minimized side reaction, co-ordinated process, high substrate conc Oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate Regulation of PDH Increased AcCoA inhibits E2 in PDH (monitors amt of energy). High AcCoA, switch off respiration, use pyruvate to switch on gluconeogenesis (formation of glycogen etc) xxxxxxx Citric Acid cycle 2C + 4C -------> 6C -----> CO2 + 4C 16 electrons The overall reaction Step1 Oxaloacetate and acetylCoA bind enzyme in open state. Enzyme changes shape, brings the reactants together and condensation occurs Step2 Step3 Step4 Step5 Cleavage of thiol energy bond and release of CoA is coupled to formation of GTP PO4 nucleophilic attack on succinate His cleaves PO4 off of succinate. PO4 transfers from His(enzyme) to GDP forming GTP Details Cleavage of thiol energy bond and release of CoA is coupled to formation of GTP PO4 nucleophilic attack on succinyl CoA releasing CoA. His cleaves PO4 off of succinate. PO4 transfers from His(enzyme) to GDP forming GTP Hydroxylation Oxidation Step6-8 Step6 Succinate dehydrogenase- uses FAD and generates FADH2. This enzyme is not in matrix but in inner mitochondrial membrane and hands FADH2 directly to the electron transport system Step7 Step8 Citric acid cycle and Anabolism Role of the citric acid cycle in anabolism. Intermediates of the citric acid cycle are drawn off as precursors in many biosynthetic pathways. Shown in red are four anaplerotic reactions that replenish depleted cycle intermediates The cycle and Anabolism Regulatory steps Regulation Glyoxylate cycle Glyoxylate and Citric acid cycle