* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3: Genetic Bases of Child Development
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Human Genome Project wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Irving Gottesman wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
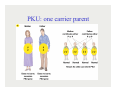
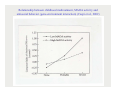
Chapter 3: Genetic Bases of Child Development Mechanisms of heredity Behavior genetics From genes to behavior Mechanisms of Heredity Genotype: the Human Genome project sequenced the base pairs (the DNA code) on all 23 chromosomes in 2003. The human genome contains 2025,000 protein-coding genes. Geneticists are rapidly figuring out what they do. PKU: non-carrier parents PKU: inherited inability to metabolize phenylalanine PKU: one carrier parent PKU – two carrier parents Behavior genetics: hypothetical example of polygenic inheritance 3.1: Behavioral Genetics Greater similarity among identical than fraternal twins is evidence for hereditary influences Plomin & Rowe’s (1979) twin study of sociability (text, p. 60-61) Plomin et al. (1997) adoption study (Kail, p. 362) Reaction Range: a genotype can lead to a range of phenotypes depending on the environment People with PKU genotype who eat a normal diet will be mentally retarded, but those who eat a special diet will have normal IQ The Relation Between Genes and Environment (adapted from Scarr & McCartney, 1983) conception Gene expression X experience evocative & active phenotype passive Gottlieb’s developmental systems model Identical twins’ intelligence test scores 6-24 months Relationship between childhood maltreatment, MAOA activity and antisocial behavior (gene-environment interaction) (Caspi et al., 2002)