* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2 need to know
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Down syndrome wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
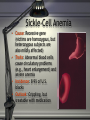
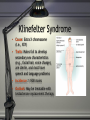
The Development Of Children Chapter 2 The Human Heritage: Genes and the Environment Bottom Line 1 Terms to know in Ch 2 • Mitosis and Meiosis • Chromosomes: Males have XY and Females have XX chromosomes • Genes • DNA • Dominant and Recessive Genes Bottom Line 2 Concepts to know in Ch 2 • Genetics + Environment = Characteristics Sex-linked characteristics • Gene-environment interaction - bunnies! • Genes and behavior - family, twin and adoption studies • Causes of Genetic Abnormalities (Down Syndrome, PKU, Sickle Cell anemia, Klinefelter Syndrome) Down Syndrome • Cause: 3 (vs. 2) copies of chromosome 21 • Traits: Mentally/physically retarded and distinctive physical characteristics • Incidence: 1:1000 births • Outlook: Special education markedly improve intellectual, social, physical and creative functioning Phenylketonuria (PKU) • Cause: Defective recessive gene resulting in retarded development of prefrontal cortex • Traits: Severe retardation • Incidence: 1:10,000 • Outlook: Feeding PKU infants a diet avoiding milk, eggs, bread, fish reduces the severity of mental retardation Sickle-Cell Anemia • Cause: Recessive gene (victims are homozygous, but heterozygous subjects are also mildly affected) • Traits: Abnormal blood cells cause circulatory problems (e.g., heart enlargement) and severe anemia • Incidence: 8-9% of U.S. blacks • Outlook: Crippling, but treatable with medication Klinefelter Syndrome • Cause: Extra X chromosome (i.e., XXY) • Traits: Males fail to develop secondary sex characteristics (e.g., facial hair, voice change), are sterile, and most have speech and language problems • Incidence: 1:900 males • Outlook: May be treatable with testosterone replacement therapy Survival Strategies: Culture • Cultural artifacts, such as tools and clothing, greatly extend the range of environments in which human beings can reproduce and thrive • Cultural knowledge, such as the creation of “hazard prevention strategies,” serves to protect and support children to enable them to mature and reproduce