* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure and Function
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
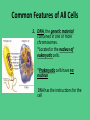
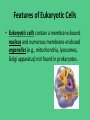
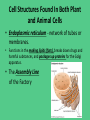
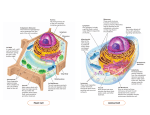
Homework and Notes Check! Cell Structure and Function Cells are like a factory…. Common Features of All Cells • All cells, whether they are prokaryotic or eukaryotic, have some common features. Common Features of All Cells 1. DNA, the genetic material contained in one or more chromosomes. *Located in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. *Prokaryotic cells have no nucleus DNA has the instructions for the cell DNA Structure Common Features of All Cells 2. Plasma membrane, a phospholipid bilayer with proteins that separates the cell from the surrounding environment * Cell membrane controls what enters or leaves the cell. Common Features of All Cells 3. Cytoplasm - basically the substance that fills the cell. It is a jelly-like material that is eighty percent water and usually clear in color. • Cell organelles are suspended and move about in the cytoplasm. http://www.learner.org/courses/essential/l ife/images/show1.cytoplasm.jpg Common Features of All Cells 4. Ribosomes, the organelles on which protein synthesis takes place http://t2.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcTqyG7jGQZ7C6SLP0K7ZmDlvb6IE5K toPYcYzxZOsOHGaH8hJLaJkMqOA0d Features of Eukaryotic Cells • Eukaryotic cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus and numerous membrane-enclosed organelles (e.g., mitochondria, lysosomes, Golgi apparatus) not found in prokaryotes. Cell Structures Found In Both Plant and Animal Cells • Cell Membrane – Phospholipid bylayer. • Controls entry and exit of materials – Shipping & Receiving • Contains proteins • Responsible for communication between cells • Also known as the “Fluid Mosaic Model” http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/media/cell_membrane.gif Cell Structures Found In Both Plant and Animal Cells • Nucleus - The large, membrane-bounded organelle that contains the genetic material, in the form of DNA molecules organized into structures called chromosomes. • Controls cell activities and passes on hereditary information. • This is the Main Office http://web.bio.utk.edu/BCMB513-4/nucleus1.jpg Cell Structures Found In Both Plant and Animal Cells • Cytoplasm - clear, thick, jellylike material and organelles found inside cell membrane. • Supports and protects cell organelles. • This is the Factory Floor Cell Structures Found In Both Plant and Animal Cells • Endoplasmic reticulum - network of tubes or membranes. • Functions in the making lipids (fats), breaks down drugs and harmful substances, and packages up proteins for the Golgi apparatus. • The Assembly Line of the Factory Cell Structures Found In Both Plant and Animal Cells • Endoplasmic reticulum – • Two types: 1. (RER) Rough endoplasmic reticulum – Dotted with ribosomes. 2. (SER) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum – not covered with ribosomes. Cell Structures Found In Both Plant and Animal Cells • Ribosomes – Free floating or attached to ER. • Site of protein synthesis • These are the Employees of the Factory http://bass.bio.uci.edu/~hudel/bs99a/lecture22/rough_er -em.gif Cell Structures Found In Both Plant and Animal Cells • Golgi Apparatus - Makes and transports proteins and other materials out of the cell • Finishing and Packaging of the Factory where products are processed and shipped out Cell Structures Found In Both Plant and Animal Cells • Mitochondria – “Powerhouse” of the cell. • Site of cellular respiration which produces energy (ATP) that can be used by the organism for life functions. • Cell’s Power Plant Cell Structures Found In Both Plant and Animal Cells • Vacuole – One large central vacuole in plant cells, many smaller vacuoles in animal cells. • Storage of food, water, waste. • Cell’s Warehouse Cell Structures Found Only In Animal Cells • Lysosome - small, round, with a membrane. • Breaks down larger food molecules into smaller molecules • Digests old cell parts • “Garbage Truck” of the cell • The Custodians http://i300.photobucket.com/albums/nn2/aysh_photo/lysosome.png Cell Structures Found Only In Plant Cells • • • • Cell Wall - outer layer Rigid, strong, stiff Made of cellulose Supports and protects the plant cell. • This is what Robert Hooke saw when he first looked at dead cork cells. http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/plants/images/plantcell.jpg Cell Structures Found Only In Plant Cells • Chloroplasts - green, oval usually containing chlorophyll (green pigment). • Uses energy from sun to make food for the plant (photosynthesis). http://207.239.98.140/UpperSchool/Science/Classes/AllBiology/bio/biotext/biowils on/images/Chloroplasts_face_side_MC.jpe