* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Motor neuron
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Neurocomputational speech processing wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
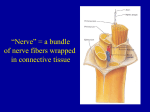
Functions of the Spinal Cord • Transmit • Transmit • Integrate Sensory Info Brain Spinal Cord Motor Commands Periphery Transmitting Information Ascending tracts Fasciculus gracilis Dorsal Fasciculus cuneatus white column Dorsal spinocerebellar tract Ventral spinocerebellar tract Lateral spinothalamic tract Ventral spinothalamic tract Descending tracts Ventral white commissure Lateral reticulospinal tract Lateral corticospinal tract Rubrospinal tract Medial reticulospinal tract Ventral corticospinal tract Vestibulospinal tract Tectospinal tract Stimulus Integration - Reflexes Skin 1 Receptor Interneuron 2 Sensory neuron 3 Integration center 4 Motor neuron 5 Effector Spinal cord (in cross section) Bone Spinal Cord Protected by Meninges Cerebrospinal fluid Bony Protection Meninges 3 Membranes surrounding the spinal cord Pia mater Arachnoid mater Dura mater Meninges Basic Arrangement Spinal Cord Pia mater Arachnoid mater Dura mater Epidural space Subarachnoid space CSF Functions: 1. Support 2. Protect 3. Buffer Produced from blood by specialized capillaries (choroid plexuses) in the brain Spinal Cord Anatomy Foramen magnum – L1 Cervical nerves C1 – C8 Thoracic nerves T1 – T12 31 spinal nerve pairs 31 spinal segments Lumbar nerves L1 – L5 Sacral nerves S1 – S5 Coccygeal nerve Co1 C2 C3 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C4 C5 T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 T2 C6 C6 C7 T2 T8 T9 T10 T11 C5 L1 C8 L2 T12 S2 S3 T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 T8 T9 T10 C5 C6 C8 S1 L2 L4 L1 C8 L2 S3 S4 S5 C6 C7 S2 S2 S2 C6 C7 C8 S1 L1 L3 L5 L4 T11 T12 L1 L3 L5 C7 C6 S1 L3 C5 L2 L5 L4 L3 L5 L5 L4 S1 S1 L4 L5 L4 L5 S1 Spinal Cord Anatomy Conus Medullaris & Cauda Equina Filum Terminale Spinal Cord – Cross Sectional Anatomy Gray Matter – Somata Dendrites Unmyelinatedaxons White Matter – Myelinated axons Spinal Cord – Cross Sectional Anatomy White columns Dorsal column Ventral column Lateral column Gray commissure Dorsal horn Ventral horn Lateral horn Gray matter Central canal Spinal Cord – Cross Sectional Anatomy White Matter – Organized into columns and tracts Ascending tracts Fasciculus gracilis Dorsal Fasciculus cuneatus white column Dorsal spinocerebellar tract Ventral spinocerebellar tract Lateral spinothalamic tract Ventral spinothalamic tract Descending tracts Ventral white commissure Lateral reticulospinal tract Lateral corticospinal tract Rubrospinal tract Medial reticulospinal tract Ventral corticospinal tract Vestibulospinal tract Spinal Cord – Cross Sectional Anatomy Gray Matter Organization Dorsal root (sensory) Dorsal horn (interneurons) Dorsal root ganglion Somatic sensory neuron Visceral sensory neuron Visceral motor neuron Somatic motor neuron Spinal nerve Ventral root (motor) Ventral horn (motor neurons) Interneuronsreceiving input from somatic sensory neurons Interneuronsreceiving input from visceral sensory neurons Visceral motor (autonomic)neurons Somatic motor neurons Basic Structure of a Nerve Endoneurium Axon Myelin sheath Perineurium Epineurium Fascicle Spinal Nerve Anatomy Spinal Nerve Anatomy Ventral ramus Dorsal ramus Motor and sensory signals to/from the posterior trunk Dorsal ramus Ventral ramus Motor and sensory signals to/from the anterior trunk and limbs Ventral ramus Rami communicantes – carrying autonomic nerve fibers All ventral rami (Except T2-T12) Form Interlaced bundles of nerve fibers Nerve Plexuses 4 major plexuses Primarily serve the limbs Cervical Plexus Brachial Plexus Lumbar Plexus Sacral Plexus Mostly cutaneous nerves Cervical Plexus Ventral rami Segmental branches Lesser occipital nerve Greater auricular nerve Transverse cervical nerve Ansa cervicalis Phrenic nerve Supraclavicular nerves Ventral rami: C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 Brachial Plexus Supplies the upper limb C4 C5 C6 C7 Gives rise to several important nerves Axillary Musculocutaneous Radial Ulnar C8 T1 Axillary Nerve Carries sensory info from the shoulder region and motor commands to the deltoid muscle. Musculocutaneous Nerve Carries sensory info from the lateral arm and motor commands to the biceps brachii and brachialis muscles. Radial Nerve Carries sensory info from the posterior arm and motor commands to the triceps brachii, wrist extensors and brachioradialis muscles. Ulnar Nerve Carries sensory info from the palm and the medial hand/fingers and sends motor commands to the wrist flexors and intrinsic hand muscles. Part of the lumbosacral plexus Lumbar Plexus Supplies much of the lower limb L1 L2 Femoral Gives rise to several important nerves L3 Obturator L4 Obturator Femoral L5 Femoral Nerve Carries sensory info from much of the thigh, leg, and foot and sends motor commands to quadriceps femoris muscles. Obturator Nerve Carries sensory info from the thigh and sends motor commands to adductor muscles. Sacral Plexus Part of the lumbosacral plexus Gives rise to several Supplies much of the pelvis, thigh, and leg Superior gluteal L4 Inferior gluteal Pudendal Superior gluteal L5 S1 Inferior gluteal S2 S3 S4 Pudendal Sciatic S5 Co1 Sciatic Sciatic Nerve Carries sensory info from the skin of much of the lower limb and sends motor commands to hamstring muscles as well as other muscles of the lower leg Sciatic and feet. Gluteal Nerves Primarily send motor commands Superior gluteal to adductor muscles of the thigh Inferior gluteal and to the gluteus maximus. Pudendal Nerve Carries sensory info from the external genitalia and supplies motor commands to the external urethral and anal sphincters. • From sensation to perception Sensation is the awareness of changes in the internal and external environment • Perception is the conscious interpretation of those stimuli Neural integration 1. Receptor level 2. Circuit level 3. Perceptual level Motor control Reflex arc Stretch reflex Flexor reflex (withdrawal reflex) pain contraction Chapter 11 -Peripheral Nervous System Consists of all nervous tissue found outside the CNS Nerves (white), ganglia (gray), sensory receptors Two subdivisions - Sensory ( afferent ) and Motor ( ) efferent Motor further subdivided into _________ autonomic and _________ somatic Ganglion Nerve Ganglion Nerve Autonomic involuntary Visceral receptors Effector – smooth muscle Ganglion Cutaneous receptors Somatic voluntary Effector -skeletal muscle Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) conscious effort • functions without _________ visceral activities • controls _______ smoothmuscle, _______ cardiacmuscle, and _____glands • regulates ______ gangliaoutside CNS • efferent fibers typically lead to _______ Two Divisions Sympathetic • ____________– prepares body for fight or flight situations Parasympathetic – prepares body for resting and digesting activities • _______________ Sympathetic Anatomy Sympathetic fibers arise from lateral horns of Thoracolumbar T1 to L2 regions ________ Organ with only pre ganglionic Adrenal gland stimulation______________ Note the sympathetic chain ganglia Match Parasympathetic fibers arise from Craniosacral regions Four cranial nerves with parasympathetic fibers are … S2 – S4 Sacral region is _______ Organs with no parasympathetic? Which has more widespread influence? parasympathetic or sympathetic Parasympathetic Anatomy Somatic ____ one motor neuron _____ganglia no skeletal muscle effector _____________ Somatic Autonomic Autonomic _____motor neurons two ganglion synapse between neurons occurs within a _________ glands ________________________ smooth and cardiac muscle effectors ______, Neurotransmitters - ACh (cholinergic) and Norepinephrine (adrenergic) • Parasympathetic preganglionic fibers release ____;ACh postganglionic ____ ACh ACh norepinephrine • Sympathetic preganglionic fibers release ____; postganglionic ____________ ACh • Somatic release at neuromuscular junction ____ Comparison of Somatic Pathways to Autonomic Pathways Actions of Autonomic Neurotransmitters depend on receptor Cholinergic receptors - bind to acetlycholine • nicotinic - always excitatory • muscarinic – usually excitatory • atropine blocks (dilates pupil; salivary secretion) • pilocarpine activates parasympathetic effects Adrenergic Receptors - bind to norepinephrine • alpha - responses vary by effectors • beta – responses vary by effectors • beta 1 -increases heart rate; rennin secretion; fat metabolism • beta 2 - dilates blood vessels & bronchioles