* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIO 131
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
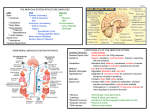
BIO 131 Unit 3 Exam Review Trunk Movements (and special terminology) Extension Flexion Lateral Flexion Rotation ?? • Which Muscles perform each action? • Innervations of the muscle groups? • Synergists/Antagonists ?? ?? Thigh & Leg Movements (and special terminology) Thigh Leg Flexion/Extension Adduction/Abduction Lateral/Medial Rotation Flexion/Extension Rotation Which muscle helps with this? Why is this necessary? Which muscles perform these actions? ?? ?? ?? Compartmental Innervations? Ankle & Foot movements (and special terminology) Ankle & Foot Plantarflexion/dorsiflexion What joint? Inversion/eversion ?? What joint? ?? Which muscles perform these actions? Vs. Compartmental Innervations? ?? Layers of the foot 1st layer: AbDM, AbH & FDB 2nd layer: 2 tendons (??), QP, L’s 3rd layer: FHB, FDM & AdH 4th layer: Interossei (dorsal & plantar) Innervation? Spinal Cord • Meningeal layers? • Where is CSF? • 2 structures derived from pia • Afferent/Efferent? • Location of neuron cell bodies? • Spinal nerve Rami ventral vs. dorsal • Length of spinal cord? Lumbar Cistern? Brachial & lumbosacral plexuses Brachial Lumbosacral RTDCB C5-T1 Lumbar L1-L4 Femoral & Obturator (L2-4) Sacral (L4-S4) Lumbosacral trunk (L4&L5) Loss of function due to injury Sciatic: Lumbosacral + S1-3 Cells of the Nervous System 2 main types Surround/support cell bodies in ganglia Satellite Schwann Neurons 2 types in PNS Supporting Cells have Cell body 4 types in CNS= neuroglia Spaces btwn = Oligodendrocytes Form myelin sheath in CNS Ependymal Ciliated, help form/circulate CSF Both can form Nodes of Ranvier Astrocytes Anchoring Nourishment crtl chem environment CNS Processes Bundles = PNS Groups of = in PNS in CNS Ganglia Nuclei Microglia Microphages clean up neural debris/micro-orgs Many inputs = Nerves One output = Dendrites do not have Tracts Axon vary in often have Myelin Sheath increases conduction speed no C Viscera, some pain/touch light B Viscera, cut. pain Site of AP generation in saltatory conduction thick A affects diameter SS & Motor Synapses (nervous system) & Neurotransmitters Electrical-ion flow from one cell to another Chemical-neurotransmitters Ach Biogenic amines Catecholamines (dopamine, NE, E) Indolamines (Serotonin, histamine) Amino acids GABA & Glycine- inhibitory Glutamate- excitatory Peptides (endorphins & Substance P) Other (ATP, NO) EPSP-Causes AP (Na+/K+…in/out?) IPSP- suppresses AP (Cl-…in or out?) Reflexes Reflex arc- rapid, automatic responses to stimuli Components: Stimulus Receptor- translates stimulus into AP Sensory Neuron-carries AP to CNS Integration center-CNS Motor neuron-carries AP to effector Effector- executes appropriate response Review specific types of reflexes!