* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transgenic Organisms
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
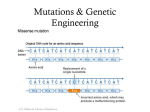
Warmup 4/13/16: Get out last night’s homework. I will collect this. On the back of yesterday’s exit ticket, write the answer to the warmup and explain why you selected this answer. Transgenic Organisms Gel Electrophoresis Gallery Walk • On a sheet of loose leaf paper… – Number 1-7 – For each number you will record answers to the questions presented at each stage of your gallery walk • We will now take a moment to go over yesterday’s homework as well as yesterday’s exit ticket. Finish Gel Electrophoresis Virtual Lab from yesterday. HOOK HOOK What is a TRANSGENIC Organisms? • Let’s break apart the word: – Trans = – Genic = – Organism = • Transgenic Organisms are: – It is an organism that has had genes inserted(or moved into) from a different organism – Transgenic organisms are made from combining different DNA What is Genetically Modified Food (GMO) • It is a crop or food that has been intentionally modified, altered or changed. What is Selective Breeding… • A type of genetic engineering • Choosing organisms (plants, animals) with the best traits (genes) and breeding them together to produce better (bigger, stronger) offspring Can you thinks of a real life example of selective breeding? Check Point 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. What is a Transgenic Organism? How are transgenic organisms made? What is a GMO? What is a real-life example of a GMO? What is selective breeding? What is a real-life example of selective breeding? Classical vs. Transgenic Breeding Discussion Questions: 1. How do modern crops compare to their ancestors? Be SPECIFIC! 1. How is modern modification different from traditional breeders? Two examples. 1. How much of our genes do we share with plants? 1. How are we able to share genes with tomatoes, insects and pigs? http://www.teachersdomain.org/resource/tdc02.sci.life.gen.breeding/ Transgenic Salmon: Super Salmon Discussion Questions: 1. How has the Salmon Been engineered? What allows transgenic salmon to grow in the winter? 1. Why would a lady salmon prefer to mate with a larger salmon? 1. What are some possible (negative) consequences of transgenic salmon escaping form their pens into the ocean population? 1. How might transgenic salmon effect the evolution of other salmon populations? 1. Do you think the FDA should give Aqua Bounty permission to grow and sell transgenic salmon? Why or why not? http://www.teachersdomain.org/resource/tdc02.sci.life.gen.salmon/ Bt Corn Discussion Questions: 1. What is the pest the farmer is trying to remove? What does the pest do to the corn? 2. How is Bt corn different than using normal pesticides? Why is it better? 3. How is Full Belly farm different? 4. What is the downside to using Bt? What happens to the pesticides over time? 5. How does planting a non-Bt area help with future resistance? http://www.teachersdomain.org/resource/tdc02.sci.life.gen.btcorn/ EOC Prep • Bacillus thuringiensis, a bacterium commonly known as Bt, produces a protein that can kill certain insects that feed on corn crops. Scientists have been successful in transferring the gene that codes for this protein from the bacterium to the corn, so the corn can now make the Bt protein. Corn borers, insects that eat corn, die when they feed on corn containing the Bt protein. A potential problem associated with increased production of Bt corn is a. b. c. d. corn borers may stop feeding on corn plants corn borers may develop resistance to the Bt protein farmers may need to use less pesticide to control corn borers corn borers may compete with other insects But how does this work…? How did THIS happen?! Glow-in-the-dark PIGS?! • A desired gene from one organism (the glow gene from a fire fly) was inserted into the DNA of a pig • Through MITOSIS the pig’s cells began replicating the glow-in-the-dark gene (the desired gene) • Let’s take a closer look at this… What is Recombinant DNA • When DNA from two different organisms come together, the DNA becomes RECOMBINANT DNA – What does recombinant (recombine) mean? • The organism that receives the recombinant DNA will use it as if it were its own DNA. Plasmid DNA: GTAACAGGCTA DNA from other organisms: ACTGTAACATT Also know as… • Transgenic Organisms How do scientists create DNA? • Its all about using BACTERIA! • This is because bacteria have DNA rings called PLASMIDS. Steps for Creating a Transgenic Organism 1. Remove the plasmid 2. Cut the bacterial DNA using restriction enzymes 1. Remove and cut a desired gene from a different organisms (foreign DNA) 2. Then glue a piece of foreign (human, plant, animal) DNA back into the plasmid using the enzyme Ligase. 3. Insert the plasmid back into the Bacteria 4. Now, the bacteria will reproduce the new gene (in the plasmid DNA) to make larger quantities of the desired gene or trait. All bacteria are… • IDENTICAL – REMEMBER: bacteria divide using asexual reproduction! • SO… Every new bacteria will be making exact copies of the desired gene! Applications of Recombinant DNA • Bacteria – used to produce hormones, antibiotics and Insulin • Plants – made to be resistant to herbicides and Pesticides • Animals – Cloning – Replacement of genes which cause disorders (aka Gene Therapy) • Such as Cystic Fibrosis • Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Genetic Engineering of Insulin Let’s take a look… • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GNMJBMt KKWU&feature=youtube_gdata_player • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TpmNfv1j KuA Genetics and Biotechnology ONE MORE TIME! Restriction Enzyme (like Eco R1) Gene (like the Insulin gene) Binary Fission to make lots of bacteria! Human Cell (like a pancreas cell) Recombinant DNA Bacterium Plasmid Bacteria cell Restriction Enzyme (like Eco R1) Each bacterium will go through protein synthesis to make lots of human insulin! Complete Side 2 of the Genetic Engineering Worksheet Transgenic Assignment Part 1: Draw and label a diagram of the creation of a transgenic organism Part 2: Then, in a minimum of 3 paragraphs (a minimum of 5-7 complete sentences per paragraph) write a essay addressing the following questions: •Describe what is happening in the image of the creation of a transgenic organism from Part 1. 1.Be sure to describe ALL steps involved in creating a transgenic organism in detail. 2.Hints: be sure to explain the importance of the shape of the bacterial DNA, your body’s “glue & scissors,” how the bacteria makes copies of itself, etc. •Explain a minimum of 2 applications/uses of transgenic organisms. 1.Hints: Why are they used? How are they used? Who uses them? •Explain the ethical implications of this biotechnology. Be sure to address each of the below questions: 1.What are some of the positive consequences of using this technology? 2.What are some of the negative consequences of this technology? 3.Do you agree or disagree with the creation and use of transgenic organisms? Why or why not? **Use your video discussion questions to help! (Transgenic vs. Traditional Breeding; Super Salmon; Bt Corn)**