* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Standard
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
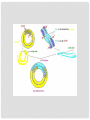
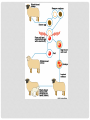
Standard: Students will analyze how biological traits are passed on to successive generations. Element: Examine the use of DNA technology in forensics, medicine, and agriculture. EQ: How is DNA technology used in agriculture? In agriculture today, farmers often produce crops or livestock that have DNA from different organisms. As you already know, inserting genes (sections of DNA) into the genome of another organism is called recombinant DNA. These inserted genes are intended to make the organisms bigger, stronger, and more resistant to disease. Organisms with recombinant genes are called transgenic organisms also known as G.M.O.'s. G.M.O. stands for Genetically Modified Organism. Most corn and soybean products sold in grocery stores in the USA are made from GMOs. In many cases, the crops have a gene added from the bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt). The gene produces an insecticide that prevents pests from eating the crop. Many food crops are engineered to be easier to grow or to be more nutritious. Bt Corn Unlike a transgenic organism, a clone is an organism that is an exact genetic copy of another organism. Their entire DNA is identical. Clones can happen naturally (twins) or artificially by Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (SCNT). Steps of Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer: 1. An egg cell is removed from an organism, placed in a petri dish, and the nucleus is removed. 2. The nucleus from a somatic (body) cell is removed and then inserted into the enucleated (without nucleus) egg cell. 3. The egg cell is then stimulated with a chemical or electric current until it starts to divide and form an embryo. 4. The embryo is then implanted into a surrogate (substitute) mother who gives birth to the newly cloned organism. Questions: 1. What is the difference between a transgenic organism and a clone? 2. What are the advantages/disadvantages of genetically modified foods?