* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells Part 2
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
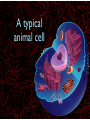
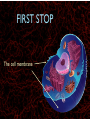
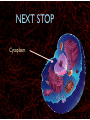
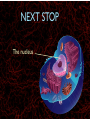
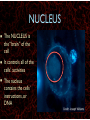
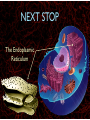
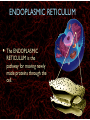
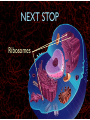
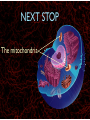
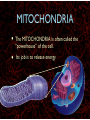
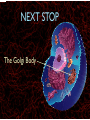
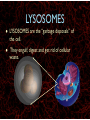
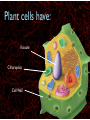
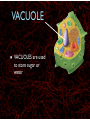
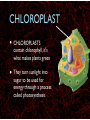
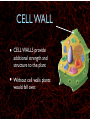
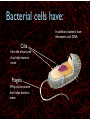
WHAT ARE YOU MADE OF? Cells Cells A typical animal cell FIRST STOP The cell membrane THE CELL MEMBRANE • The CELL MEMBRANE is the “Gate Keeper” • It controls what goes in and out of the cell. NEXT STOP Cytoplasm CYTOPLASM • CYTOPLASM is the gel- like material inside of the cell. • It provides a moist medium for materials to move. NEXT STOP The nucleus NUCLEUS • The NUCLEUS is the “brain” of the cell • It controls all of the cells’ activities • The nucleus contains the cells’ instructions, or DNA NUCLEUS • Some activities directed by the NUCLEUS include: • Making copies of itself • Making repairs • Getting rid of waste NEXT STOP The Endoplasmic Reticulum ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM • The ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM is the pathway for moving newly made proteins through the cell. NEXT STOP Ribosomes RIBOSOMES • RIBOSOMES are located both on the endoplasmic reticulum as well as free floating within the cell. • Their job is to make proteins. NEXT STOP The mitochondria MITOCHONDRIA • The MITOCHONDRIA is often called the “powerhouse” of the cell. • Its job is to release energy. NEXT STOP The Golgi Body GOLGI BODIES • GOLGI BODIES are nicknamed the “post office” of the cell. • They package up and deliver materials to be used within the cell. NEXT STOP The cytoskeleton CYTOSKELETON • The CYTOSKELETON gives the cell a stable structure. • Other important tasks: • Act as “highways” to move materials and organelles. • Pulls apart chromosomes (DNA) during cell division and replication. LAST STOP The Lysosome LYSOSOMES • LYSOSOMES are the “garbage disposals” of the cell. • They engulf, digest and get rid of cellular waste. Plant cells are a little different Plant cells have: Vacuole Chloroplast Cell Wall VACUOLE • VACUOLES are used to store sugar or water CHLOROPLAST • CHLOROPLASTS contain chlorophyll, it's what makes plants green • They turn sunlight into sugar to be used for energy through a process called photosynthesis CELL WALL • CELL WALLS provide additional strength and structure to the plant • Without cell walls plants would fall over. Bacterial cells have: In addition, bacteria have ribosomes and DNA Cilia Hair-like structures that help bacteria move Flagela Whip tail structure that helps bacteria move