* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Combustion, Addition and Elimination Objective Combustion Example
Fischer–Tropsch process wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Cracking (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Diels–Alder reaction wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
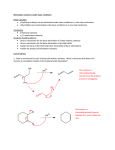
Combustion, Addition and Elimination lesson 8 chapter 14/15 Objective You will be able to identify the types of reactions that different organic molecules can undergo. Combustion The rapid reaction with oxygen. Complete combustion involves the burning (exothermic reaction) of a hydrocarbon in excess oxygen. This will produce carbon dioxide gas and water vapor. Remember to balance these in the order CHO. Example 1. Write the a balanced reaction for the complete combustion of 2-methypentane. 2. Write the reaction for the combustion of pent-2-ene. Addition Reactions Unsaturated hydrocarbon are reacted. Since the site of the double or triple carbon-carbon bond is weaker than the single bond, this bond can break and then we have free bonding electrons where another element or functional group can be added. In general: Examples Write the reaction, both structural and in a chemical equation for each of the following. Ethene reacts with chlorine gas. Propene with iodine. It may be possible to have more than one product from a reaction. Example: but-1-ene + hydrogen fluoride. Propene with water But-1-yne reacts with excess hydrogen. Testing for Unsaturated Compounds Bromine is used to test for the presence of multiple bonds. Normally bromine is brownish liquid, when added to an alkene or alkyne the color disappears. When added to an alkane no change is detected. Potassium permanganate has similar abilities, though it is not as clear cut as bromine. Elimination Reactions This like the reverse of an addition reaction. Here atoms are removed and a double bond is formed. Alcohols and alkyl halides can undergo elimination reactions. General Reaction for alkyl halides is Elimination in alkyl halides These undergo elimination in the presence of strong bases. Example: 1-chloropropane is heated in the presence of sodium methoxide. Elimination in Alcohols Alcohols undergo elimination in the presence of strong acids. General reaction is HH | | H acid H + HOH H -C-C-OH ⟶ C=C H H | | HH Example: butan-2-ol is heated in the presence of a catalyst, sulfuric acid. Assignment Read 586-593 Do practice problems #1a-c, 2a,b,d, 4,6 p. 596