* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Cracking (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Fischer–Tropsch process wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Diels–Alder reaction wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
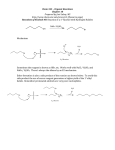
Name: ______________________________ Date: ___________________________ Reactions of Functional Groups: Alcohols and Ethers Chemical Reactions of Alcohols A) Preparing Alcohols i) Addition Hydration e.g. alkene + water alcohol H2SO4 catalyst H - C = C – CH3 + HOH H OH H - C - CH – CH3 H H H propene 2-propanol ii) Hydroxide Ion Substitution e.g. alkyl halide + hydroxide ion (from a base) alcohol + halide ion CH3CH2-Cl + OH- CH3CH2-OH + Clchloroethane ethanol chloride ion B) Other Reactions Involving Alcohols i) Combustion e.g. alcohol + oxygen water + carbon dioxide ii) Substitution e.g. alcohol + hydrogen halide alkyl halide + water CH3CH2CH2-OH + HCl CH3CH2CH2-Cl + H2O propanol 1-chloropropane water iii) Elimination e.g. alcohol (strong acid /dehydrating agent) alkene + water Chemical Reactions of Ethers Preparing Ethers Condensation alcohol + alcohol ether + water H H - C - OH H methanol + H H - C - OH H methanol H2SO4 H H H-C-O-C-H H H + HOH methoxymethane Problems 1. Name the type of reaction and draw structural diagrams to represent the following reactions: a) Reaction of propene to form an alcohol. b) Reaction of 3-methyl-2-pentanol with HBr. c) Reaction of 1-bromo-3-methylpropane with sodium hydroxide. 2. Write balanced equations and name the reactants and products for: a) dehydration (elimination) reaction of ethanol b) complete combustion of ethanol c) complete combustion of 1-propanol 3. Draw structural diagrams and write IUPAC names to represent the formation of 2-methyl-2-butanol 4. Draw structural diagrams to represent the reaction of 2-butene + water 2-butanol. Name the reaction. 5. Elimination reactions of alcohols are generally slow and require an acid catalyst and heating. i) Draw structural diagrams to represent the reaction of 1-propanol to form propene and water. ii) Write a word equation using IUPAC names for the elimination reaction (in the presence of concentrated H2SO4) CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-OH 6. Write a balanced equation to show the formation of CH3CH2CH2-O-CH2CH2CH3 (propoxypropane) from 1-propanol. Problems 1. Name the type of reaction and draw structural diagrams to represent the following reactions: a) Reaction of propene to form an alcohol. b) Reaction of 3-methyl-2-pentanol with HBr. c) Reaction of 1-bromo-3-methylpropane with sodium hydroxide. 2. Write balanced equations and name the reactants and products for: a) dehydration (elimination) reaction of ethanol b) complete combustion of ethanol c) complete combustion of 1-propanol 3. Draw structural diagrams and write IUPAC names to represent the formation of 2-methyl-2-butanol 4. Draw structural diagrams to represent the reaction of 2-butene + water 2-butanol. Name the reaction. 5. Elimination reactions of alcohols are generally slow and require an acid catalyst and heating. i) Draw structural diagrams to represent the reaction of 1-propanol to form propene and water. ii) Write a word equation using IUPAC names for the elimination reaction (in the presence of concentrated H2SO4) CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-OH 6. Write a balanced equation to show the formation of CH3CH2CH2-O-CH2CH2CH3 (propoxypropane) from 1-propanol.