* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Colorful Oxidation of Alcohol
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
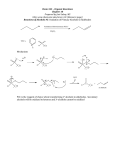
12-2 Colorful Oxidation of Alcohol Source: Summerlin, L. R., Borgford, C. L., and Ealy, J. B. (1987) Chemical Demonstrations: A Source Book for Teachers Volume 2. p. 210. Description: When a yellow solution, K2CrO7, is added to three different alcohols, the solution turns blue in two of the alcohols and remains yellow in one. Concept: Potassium dichromate will oxidize propyl alcohol and sec-butyl alcohol, but not tert-butyl alcohol. Primary and secondary alcohols are easily oxidized. The carbons holding the OH groups in propyl and sec-butyl alcohol are also holding at least one hydrogen. This hydrogen is removed by the oxidizing agent along with the H from the hydroxyl group leaving a carbonyl group and forming water. Materials: 0.015 M K2Cr2O7 in 3 M H2SO4 propyl alcohol (1-propanol) sec-butyl alcohol (2-butanol) tert-butyl alcohol (2-methyl-2-propanol) three large test tubes 25 mL graduated cylinder Stirring rods Safety: Wear safety goggles and gloves. Sulfuric acid is irritating. Potassium dichromate is extremely destructive to the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract, skin, and eyes. Exposure could be fatal. Also it is a carcinogen. Procedure: Add about 25 mL of each alcohol to the large test tubes. Add 25 mL of the K2Cr2O7 solution to each tube and stir quickly. Clean-Up: Collect the contents of the test tubes in a waste bottle, label a waste tag, and take to EH&S collection site. Notes: This demo has never been done in class. It was requested by Prof. Richardson for C102. See diagram next page for information about the reactions. 12-2 H H H H H- C- C- C- OH H H H H H (yellow) H H H H O H CH H (yellow) tert H (blue) H H O methyl ethyl ketone H O 2 H (blue) 3 HO - C - CH CH H O 2 H- C- C- C- C- H + + (O) H sec -Butyl Alcohol O + H propylaldehyde H- C- C- C- C- H H H H- C- C- C + (O) H 1-Propanol H 3 + (O) NR (no color change) remains yellow 3 -Butyl Alcohol (yellow) The aldehyde would be further oxidized to form a carboxylic acid. The ketone would not be further oxidized. Another demo in this manual, The Silver Mirror (Tollen's Test for Aldehydes) illustrates this principle 12-2