* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gene Mutations - WordPress.com
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
BRCA mutation wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
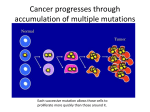
Gene Mutations D.S.Q Tuesday Feb. 23 • 1. Why do children resemble their parents? • 2. Why don’t all people look alike? Look Alike Survey What are genes? • Genes are a section in the chromosome that has genetic information • Chromosomes are made of proteins and DNA, which is an organism’s genetic material Genes • Genes are located on all chromosomes, autosomes, as well as sex chromosomes. • Each organism has a pair of each autosome, one inherited from the mother, the other inherited from the father. • Each organism also has a pair of sex chromosomes, one inherited from each parent. How is DNA structured? • DNA is like a twisted zipper, called a double helix. • It get’s its shape from the nucleotides, which is a molecule made of a nitrogen base, a sugar and a phosphate group. Mutations • A mutation is a change in a nucleotide sequence of a gene • Humans have 23 paired chromosomes (so a total of 46) and we contain 20,000-25,000 genes that are copied during DNA replication. Mistakes can happen during this process. • Mutations can be triggered by exposure to X-rays, ultraviolet light, radioactive materials and some kinds of chemicals. Mutations • If a mutation occurs in a body cell, such as a skin cell, the mutation will not be passed on to the organism’s offspring. • But if a mutation occurs in a sex cell (egg or sperm), the mutation can be passed on to an offspring and affect the offspring’s traits. Types of Mutations • • • • There are 3 types of mutations. 1. Deletion mutation 2. Insertion mutation 3. Substitution mutation Deletion Mutation • One or more nitrogen bases are left out of the DNA sequence Insertion Mutation • One or more nitrogen bases are added to the DNA Substitution Mutation • One nitrogen base is replaced by a different nitrogen base Effects of Mutations • Mutations can be harmful, helpful or neither. • A mutation is harmful if it reduces the organism’s chances for survival and reproduction • How would these two alligators affect their environment they live in? How cancer begins? • Scientists think that cancer begins when something damages a portion of the DNA in a chromosome. The damage causes a mutation and the cells to function abnormally. • Cancer begins when mutations disrupt the normal cell cycle, causing cells to divide in an uncontrolled way. How is cancer related to mutations? • Cancer is a disease in which cells grow and divide uncontrollably, damaging the parts of the body around them. • Cancer can be either inherited through your parents or grandparents or causes by substances in the environment, such as cigarettes or ultraviolet lights from the sun or tanning beds DSQ Thursday • 1. Why do doctors ask if you have a family history of certain diseases? • 2. What is a mutation? • 3. Are gene mutations always harmful to organism? • 1. Many diseases are the result of inherited traits. A doctor can predict your risk of having genetically inheritable diseases based on your family’s medical history. • 2. A mutation is a permanent change to an organisms genetic code. Mutations can occur for a variety of reasons and may result in new structural features or different functional behaviors in the affected offspring. • 3. No, not all mutations are harmful. Some mutations, such as mutations that lead to cancer, are harmful. But there are beneficial mutations such as the ability to digest lactose, higher than normal bone density, and superior color vision. Questions for Rearranging Proteins • 1. After placing the letter D in the sentence, it did not make any sense. What kind of mutation occurred? • 2. After removing the letter H from the sentence, it did not make any sense. What kind of mutation occurred? • 3. After inserting the letter D between the B and the I and rearranging the letters, the sentence did not make any sense anymore. What kind of mutation occurred?