* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protein Synthesis PPT
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
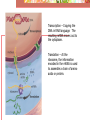
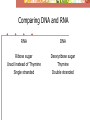
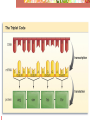
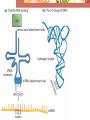
Protein Synthesis Protein or Polypeptide chain Transcription – Copying the DNA in RNA language. The resulting mRNA moves out to the cytoplasm. Translation – At the ribosome, the information encoded in the mRNA is used to assemble a chain of amino acids or protein. Comparing DNA and RNA RNA DNA Ribose sugar Uracil instead of Thymine Single stranded Deoxyribose sugar Thymine Double stranded Transcription • RNA polymerase copies the DNA strand, adding the complimentary RNA bases to form the mRNA The mRNA moves to a ribosome for translation into a protein. The Triplet Code • There are four DNA bases • They code for 20 amino acids • If two bases coded for one amino acid, there wouldn’t be enough, only 16 • Three bases coding for each amino acid is just right, 64 possible combinations. • A set of 3 DNA bases that code for one amino acid is referred to as a codon. mRNA genetic code library There are Three Forms of RNA • mRNA – messenger RNA carries the information for synthesis of protein • rRNA – ribosomal RNA makes up ribosomes • tRNA – brings the amino acids to the ribosome for protein synthesis • The triplet code in tRNA is called the anticodon • Each tRNA and its anticodon is specific for one amino acid Translation • mRNA binds to the ribosome • tRNA arrives, binding to the ribosome • A 2nd tRNA arrives, their amino acids bond and the 1st tRNA leaves • More tRNA arrive until the mRNA is completely translated into protein Mutations • Mutation – a permanent alteration of a DNA base sequence • Most have no effect on an organism. Some have a deadly effect, only a slight few have a positive effect. • Point mutation • When a single base pair is changed. • Whole chromosome mutations • See chapter 12 • Most mutations happen in somatic cells and are of little or no importance. • Melanoma or skin cancer • Mutations that happen in gametes can be passed from generation to generation. A Pedigree of Hemophilia in the Royal Families of Europe Selected members of the pedigree I-1 = King George III III-1 and III-2 = Prince Albert and Queen Victoria IV-5 and IV-6 = Alice of Hesse and Ludwig IV of Hesse V-13 and V-14 = Alix and Nicholas II (Tsar of Russia) VI-16 = Alexei