* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Transport Notes
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
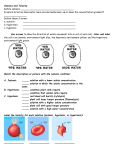
Cell Transport Notes In a way a cell is like a miniature version of you. It requires nutrients and, in the process of breaking down the nutrients, the cell produces wastes. So there has to be a way to get nutrients in and wastes out. This process in cells is called ______________________. The organelle responsible for cellular transport is the _______________ ______________________. General Terms: Concentration gradient – The _________ distribution of particles. Osmotic Pressure – the ______ pressure in cells Turgor pressure – the water pressure in ________ cells Plasmolysis – Process where the cell membrane _________ from the cell wall due to water loss. What causes plasmolysis? (a___________ solution) Hypotonic Hypotonic Hypotonic Isotonic Isotonic Isotonic Hypertonic Hypertonic Hypertonic 2 Types of Transport Passive – Active – Types are: Diffusion – Types are: Endocytosis – Osmosis – Exocytosis – Facilitated Diffusion - Type of Transport Transport Protein Used? Direction of Movement? Needs Active or Energy? Passive? Osmosis Simple Diffusion Facilitated Diffusion Exocytosis Endocytosis Why are cells so small? As the volume of a cell (the inside of the cell with all of the working organelles) increases, the surface area (the cell membrane) doesn’t increase as much. So……. The cell membrane can’t diffuse enough nutrients in and wastes out to maintain a larger volume, so cells have adapted by increasing the surface area thus increasing the surface area to volume ratio. Cell Transport Practice Label each of the blood cells according to the type of solution that they must have been placed into. Label each of the solutions surround the cell as hypertonic, isotonic, or hypotonic. Give everyday examples of the following solutions compared to a human body cell. Hypertonic:____________________________________________________ Isotonic:_______________________________________________________ Hypotonic:_____________________________________________________