* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 10 - WTPS.org
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
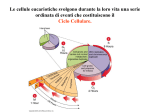
CP Biology Final Review Turning Point/Power Point Review Please select a Team. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Darwin Lamarck Malthus Lyell Hutton Sunlight, water and carbon dioxide are combined into sugars during A. Respiration B. Cellular respiration C. Protein synthesis D. Photosynthesis sis th e ho to sy n in Pr ot e C. rr es llu la Ce D. P sy nt he tio pi ra ra t Re sp i B. sis n io n 25% 25% 25% 25% A. • • • • Organisms that can make their own food are: hs ro p tro ph 25% Fu ng i 25% s 25% nt o Ph e ot ro ph s 25% Au to t Heterotrophs Phentotrophs Autotrophs Fungi He te r a. b. c. d. Photosynthesis is affected by A. Light intensity B. Oxygen C. sugar D. starch ch ta r D. s C. su ga r Ox yg en B. L ig ht in te ns ity 25% 25% 25% 25% A. • • • • Cellular respiration releases rg y rc h St a Su ga B. 25% ne 25% D. E 25% r 25% C. Oxygen Sugar Starch Energy Ox yg en A. B. C. D. A. • • • • The reactants for cellular respiration are • A. Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide\ • B. Carbon Dioxide and Water • C. Water and Oxygen • D. Oxygen and Sugar ga r xy g en an d Su Ox yg e D. O C. W at er e Di ox id on Ca rb B. an d an d bo n Ca r d an Ox yg en A. . .. D. .. n 25% 25% 25% 25% 2 ATP molecules are produced during • A. Glycolysis • B.. Photosynthesis • C. Cellular Respiration • D. Respiration Ce llu n D. Re s pi ra tio io n ra t Re sp i lar sy nt he s is C. B. .P ho to A. Gl y co l ys is 25% 25% 25% 25% The type of fermentation that occurs in muscles is Lactic Acid Alcoholic Mitochondrial Lysosomic ic D. L ys os om l nd ria ch o ito M C. B. Al ic co h Ac id ol ic 25% 25% 25% 25% La ct A. B. C. D. A. • • • • When ATP releases energy, what type of bond is broken High Energy Low Energy Medium Energy All of the Above Ab ov e er gy ft he En D. A ll o m M ed iu C. B. Lo w En er En er gy gy 25% 25% 25% 25% Hi gh A. B. C. D. A. • • • • The waste product of Krebs cycle is A. Energy B. Oxygen c. Carbon Dioxide d. Sugar Ca r c. Su ga r d. bo n Di o xid e Ox yg en B. En er g y 25% 25% 25% 25% A. • • • • A heterotroph is an organism that 33% Au to tr op h 33% Is a n Pr o Is a B. A. Is a co ns um er du ce r 33% C. • A. Is a consumer • B. Is a Producer • C. Is an Autotroph In which phase of mitosis do chromosomes become visible? 1. 2. 3. 4. Prophase Interphase Metaphase Telophase 30 Which of the following is a phase of mitosis? 1. 2. 3. 4. Cytokinesis S phase Telophase Interphase 25% 25% 25% 25% 0 Cytokinesis S phase Telophase Interphase The “father” of Genetics is? 1. 2. 3. 4. Darwin Mendel Franklin Watson 25% 25% 25% 25% Darwin Mendel Franklin Watson 10 Two plants with the genotype YY and Yy 1. Have all dominant alleles 2. Have all recessive alleles 3. Would have the same phenotype 4. Would have different phenotypes ... nt p ffe re ve ha W ou ld ve ha W ou ld di th e ec lr al Ha ve p. .. e sa m e es siv in om ld al Ha ve el all an ta lle le s es 25% 25% 25% 25% 10 What process produces gametes? 1. 2. 3. 4. Meiosis Crossing over Mitosis Replication 25% 25% 25% 25% 10 Meiosis Crossing over Mitosis Replication When one allele is not completely dominant over another it is called… 1. Multiple alleles 2. Codominant alleles 3. Incomplete dominance 4. Multiple genes 0 of 30 25% 25% 25% 25% Multiple alleles Codominant alleles Incomplete domina... Multiple genes Mendel allowed the F1 generation to self-pollinate, the offspring were… Medium height All tall All short Some tall & some short sh o e so m l& ta l e So m 10 rt sh or t Al l l ta l Al l ed iu m he ig ht 25% 25% 25% 25% M 1. 2. 3. 4. Mendel used pea plants to study… 1. How to raise the best peas 2. How plant gametes are formed 3. The inheritance of traits 4. How plants cross 10 pollinated 25% 25% 25% 25% How to raise the ... How plant gametes... The inheritance o... How plants cross ... Meiosis results in cells called Ce lls ls Ce l id 25% Bo dy 25% et es 25% Ga m at ic Ce lls 25% Di pl o Somatic Cells Gametes Diploid Cells Body Cells So m 1. 2. 3. 4. The principles of genetics apply to 1. 2. 3. 4. Biotic Factors Plants Animals Abiotic Factors 25% 25% 25% 25% Biotic Fac... Plants Animals Abiotic Fa... Cells produced during meiosis are _____, cells produced during mitosis are______ . 1. 2. 3. 4. Diploid, haploid 2n, n Haploid, diploid Somatic, gametes 25% 25% 25% 25% Diploid, haploid 2n, n Haploid, diploid Somatic, gametes A DNA nucleotide consists of: rib up , gr o up , Ni tro g en gr o en Ni tro g os e, ... xy r. . . de o rib gr ou p, te Ph os ph a te gr ou p, de o xy ... os e, .. . 25% 25% 25% 25% Ph os ph a 1. Phosphate group, deoxyribose, nitrogenous base 2. Phosphate group, ribose, nitrogenous base 3. Nitrogen group, deoxyribose, phosphate base 4. Nitrogen group, ribose, phosphate base RNA contains the sugar 1. 2. 3. 4. Deoxyribose Glucose Fructose Ribose 25% 25% 25% 25% Deoxyribose Glucose Fructose Ribose What is the process of translation? 1. DNA is made from mRNA 2. mRNA is used to make proteins 3. DNA is copied 4. rRNA is used to make proteins 25% 25% 25% 25% DNA is mad... mRNA is us... DNA is cop... rRNA is us... Mutations of one nucleotide are called 1. Chromosomal mutations 2. Translocation 3. Inversion 4. Point mutations ns n Po i nt m ut at io rs io In ve ca t slo Tr an Ch ro m os om al m ut at io ns io n 25% 25% 25% 25% A normal human male has ______ chromosomes and ____ sex chromosomes 25% 46 ,X Y 25% 46 ,X X 25% 23 ,X X 23, XY 23, XX 46, XX 46, XY 23 ,X Y 1. 2. 3. 4. 25% Sickle-cell disease in a human is caused by 1. A single gene change in DNA that results in different amino acids 2. A multiple gene change in DNA that results in different amino acids 3. A single gene change in DNA that results in the same amino acids 4. A multiple gene change in DNA that results in the same amino acids A single g... 25% 25% 25% 25% A multiple... A single g... A multiple... Endosymbiotic theory suggests that eukaryotic cell developed from ro k tie so rp la Co m m un i lu ce l ul ti M 33% ry ot es ar y ot e by .. . ed m sf or tie un i m Co m 33% s 33% fe uk a 1. Communities formed by prokaryotes 2. Multicellular prokaryotes 3. Communities of eukaryotes In this world of woe and sin, your head grows bald, but not your hi n 25% D. C 25% No se Kn ee 25% B. bo w 25% C. Elbow Knee Nose Chin El A. B. C. D. A. • • • • The first organisms on Earth were most like today’s 1. Bacteria 2. Eukaryotes 3. Multicellular organisms 4. DNA Molecules s ol e M DN A rg a ro la ce llu ul ti cu le ni sm s s ar yo te Eu k M Ba ct er ia 25% 25% 25% 25% Sharks, dolphins and penguins all have streamlined bodies and appendages that enable them to move through water. This is a result of 33% 33% 33% n nt ev ol u tio ct io n rp ro du Co ev ol ut io n 1. Coevolution 2. Asexual rerproduction 3. Convergent evolution Genetic variation or gene shuffling are most often the result of Mutations Mitosis Adaptations Sexual reproduction Se x ua l re p Ad a pt a ro du ct tio io n ns sis ito M ut a tio ns 25% 25% 25% 25% M 1. 2. 3. 4. In humans the tailbone is an example of Analogous structure Natural variation Vestigial structure Homologous structure tru ct og ou ss ial Ho m ol tig Ve s ur e e uc tu r st r ar ia lv ur a Na t lo go us st r uc t t io n ur e 25% 25% 25% 25% An a 1. 2. 3. 4. The Earth is believed to be how old ? io bi ll 4. 5 bi ll io n on illi m 50 n ye ar s ar s ye ar ye io n m ill 25% ye ar s 25% 25% s 25% 3. 5 3.8 million years 50 million years 3.5 billion years 4.5 billion years 3. 8 1. 2. 3. 4. It is believed that life on Earth began 1 million years ago 2 million years ago 3.5 billion years ago 10 billion years ago bi ll 10 io bi ll 3. 5 io n n ye a ye ar s rs ag ag o o o ag ye ar s n io 2m ill io n ye ar s ag o 25% 25% 25% 25% 1m ill 1. 2. 3. 4. Which type of mutation results in an extra chromosome in a human karyotype 25% 25% 25% n at io du pl ic io n Tr an slo ca t io n sju nc t No nd i m es hi ft Frameshift Nondisjunction Translocation duplication Fr a 1. 2. 3. 4. 25% The mutation which results if one or more nucleotide was added to DNA m es hi ft 25% Fr a t io n 25% ica io n 25% sju nc t No nd i rs io n 25% Du pl Inversion Nondisjunction Duplication Frameshift In ve 1. 2. 3. 4. Just as whales have vestigial leg & hip bones, humans have which of the following organs that are vestigial? ... ve s ab ov he Al l of t s li Gi ll ea pi nk ts & an & s bo ne Ta il re pe nd ap le g & Ar m yf in ge ix bo ne s 1. Arm & leg bones 2. Tail bones & an appendix 3. Gill slits & pinky fingers 4. All of the above are vestigial in humans rs 25% 25% 25% 25% 10 Which of the following scientist presented research that showed that the earth changed over many millions of years? 1. Charles Darwin 2. Francesco Redi 3. James Hutton & 25% 25% Charle’s Lyell 4. Thomas Malthus & Lynn Margulis 25% Charles Da... Francesco ... 25% James Hutt... 10 Thomas Mal... When allele frequency in a population remains constant this is called_________ and it involves _______selection. e up tiv at ur ta b Ge ne po ol vig Cl o or ; ni n di sr g; n ;s r iu m eq Ge ne tic Ge ne tic dr ui lib ift ;d ire ct io na ... l 1. Genetic drift; directional 2. Genetic equilibrium; stablizing 3. Cloning; natural 4. Gene pool vigor; disruptive al 25% 25% 25% 25% 10 Which best describes a mutation? 10 1. A change in phenotype, but not genotype 1. A change in genotype, but not phenotype 2. A change in the sequence of DNA 3. A change in the rate of the reproduction of cells 25% 25% 25% 25% A change in pheno... A change in genot... A change in the s... A change in the r... A good example of geographic isolation of a gene pool ef fe ct of be Ha in gs bi ta ep tf a. ra .. gm en Lo ta ng tio n w th in ge .. d fli es all m of at th in e ... ab ov ea re ex a. .. 25% 25% 25% 25% th e 1. the effect of being separated on an island 2. Habitat fragmentation that prevents panda bears from mating 3. Long winged flies mating with only other long winged flies due to higher height of flight 4. all of the above are examples 10 Half –life is described as 25% 25% 25% 25% Ti m bo ve ... th ea pe r io No ne of a fo r ei tt ak es lif es Th e ou nt o ft im e pa n it of ta k es .. . af os s il 0 of 30 Am 1. Amount of time it takes for half of the radioactive material in a dead organism to decay 2. The life span of a fossil 3. Time it takes for a period of geological to elapse 4. None of the above Which of the following concepts is NOT part of Darwin’s natural selection theory? 10 1. Competition for resources 2. Variations exist in each and every species 3. Survival of the fittest 4. Inheritance of acquired characteristics 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% Competition for r... Inheritance of ac... Variations exist ... Survival of the f... Which of the following is the proper eras of time in order from most recent to distant past? 10 1. Precambrian, paleozoic, mesozoic, cenozoic 2. Cenozoic, meosozoic, paleozoic, precambrian 3. Paleozoic, mesozoic, cenozoic, precambrian 4. Meoszoic, precambrian, paleozoic, cenozoic 25% 25% 25% 25% Precambrian, pale... Cenozoic, meosozo... Paleozoic, mesozo... Meoszoic, precamb...