* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Week 1, Cells, Jan 17, student version
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
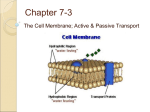
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cells Chapter 3 Cells • Basic organizational structure of the human body • About 75 trillion cells in our bodies • Can look and function quite differently Differentiation • When cells specialize • Specialize in function and form Cells • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gFuEo2cc TPA Typical animal cell • Many organelles with distinct roles (ex: mitochondria, nucleus, etc.) Cell (plasma) membrane • Important in physiology • Allows stuff in and out of the cell, so the cell can perform it’s function • But, it’s selectively permeable, meaning that only certain stuff can go in and out Cell (plasma) membrane • Phospholipid bilayer • Embedded proteins • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qqsf_UJcf Bc Movement across cell membranes • Materials must cross the membrane • Metabolism of the organism occurs within the cell. • Important molecules such as carbon dioxide, sugars, oxygen, and nutrients must move into and out of the cell. Movement across the membrane • Can be passive- no input of energy – Simple and facilitated diffusion – Osmosis • Or active- necessitates energy to move stuff – Active transport – Endocytosis – Exocytosis – Transcytosis Simple diffusion • Movement of material from an area of higher to lower concentration Simple diffusion Simple diffusion Simple diffusion • Selectively permeable Factors that affect the rate of diffusion • Concentration • Temperature • Size of molecule • Charge of molecule Osmosis • Same thing as simple diffusion, just with water Osmotic pressure • Force exerted on a selectively permeable membrane due to osmosis • We want the concentration of sugar and water to be equal between the two containers • There’s too much sugar on the right side • The only way to equalize is to move water (sugar is too big to pass through) Tonicity • Degree to which a solution’s solute concentration causes water to move into or out of cells Solution Salt water - Hypotonic - Hypertonic - Isotonic = Solvent + Solute water Solution types Facilitated diffusion • Maybe the molecule is too big (sugars, salts) • Transmembrane proteins can come to the rescue! • Still moving from a higher to a lower concentration • No energy required Active transport • Particles are moved against the concentration gradient • Requires energy!!! Actively climbing against gravity requires energy. Active Transport • Movement of a substance against the concentration gradient • Uses a carrier protein and energy (ATP) • Examples: ions, amino acids, and sugars Endocytosis • Bulk transport • Movement across the membrane and into the cell using vesicles • Requires energy Exocytosis • Bulk transport • Movement across the membrane and out of the cell using vesicles • Requires energy Transcytosis • Endo, followed by exocytosis • Moves substances rapidly