* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Cells
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
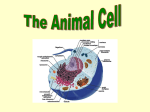
INTRODUCTION TO CELLS Worksheet Answer Keys CELL FUNCTIONS ANSWER KEY EAT For Protein Storage Tank Fashion ~ Plus Enter Exit LIFE’S MINIATURE FACTORY Cell Structure Function 1. Mitochondrion “Burns” fuel to produce energy 2. Chloroplasts Use the energy from sunlight to produce food, such as sugar, from raw materials 3. Cell Membrane Determines what will enter and/or leave. 4. Chromatin Contains the “blueprints” of the cell. Cell Structure Function 5. Nucleus Directions the functioning of all of the other parts 6. Endoplasmic Reticulum Moves materials from place to place. 7. Vacuole Neatly Stores materials until they are needed 8. Lysosome Breaks down items so that they are easily useable. CELLS VOCABULARY Word Definition Word Definition 1. Tissue G 7. Cell Wall J 2. Vacuole C 8. Nucleolus F 3. Chromosome H 9. Organ B 4. Chlorophyll I 10. Cytoplasm D 5. Cell Membrane L 11. Nucleus A 6. Chloroplast 12. Mitochondrion E K LOOKING INSIDE CELLS (21E) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. cytoplasm endoplasmic reticulum nucleus mitochondrion cell membrane 6. Tissue--a group of similar cells that work together to perform a function 7. Chloroplast -- an organelle that uses light to make food in plants 8. Ribosomes -- an organelle that makes proteins 9. Nucleus -- the control center of the cell 10. Mitochondrion -- an organelle that breaks down food to make energy 11. Organ -- a group of different tissues that function together 12. Multicellular -- made up of many cells CELL STRUCTURE (WS27) 1-11 Cell Part Function 1. Cytoplasm Gelatin-like mixture that flows inside the cell membrane. Cell Membrane 2. Allows certain materials to enter and/or exit the cell. 3. Nucleus Directs all cell activities Endoplasmic Reticulum 4. Moves materials around the cell. 5. Ribosomes Makes proteins 6. Mitochondrion Releases energy stored in food Chloroplasts 7. Captures light energy and converts it to chemical energy in plants. Cell wall 8. Outer cellulous structure in plants that protects the cell. 9. Vacuole Stores water, waste products, food and other cellular materials Golgi bodies 10. Packages and sorts cellular substances for export. 11.Lysosomes Breaks down food molecules, cell wastes, and worn-out cell parts. CELL STRUCTURE (WS27) 12-21 STOP HERE FOR TODAY COMPARING PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS (GRAPHIC ORGANIZER) Lysosomes Ribosome Nucleus Nucleolus Vacuole Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Cell Membrane Mitochondrion Cytoplasm Golgi Body Cell Wall Chloroplasts COMPARING PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS (ANALYSIS) 1. Name two things found in a plant cell that are not found in an animal cell: 2. How does the shape of a plant cell differ from that of an animal cell? 3. What is the function of the chloroplasts? 4. What is the function of the vacuole? 5. Why don’t animals require chloroplasts? 6. Why do plants require cell walls? 7. Why do plants need larger vacuoles than animals? STUDY FOR YOUR TEST FRIDAY!!!