* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BELL WORK: Answer the following questions:
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
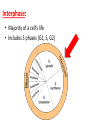
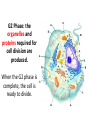
Happy Friday! BELL WORK: Write the questions below AND your answers and highlight/underline key words: 1. What is the product of the process of TRANSLATION? a) b) c) d) A complementary mRNA strand Increased production of ribosomes A completed protein Replacement of disabled nucleotides 2. A mutation is LEAST LIKELY to affect a cell when the mutation – a) Reverses the order of bases in a DNA strand b) Allows the total number of bases in a DNA sequence to remain the same c) Replaces a base with its complementary base d) Produces a codon that codes for the same amino acid as the original codon Happy Friday! BELL WORK: Write the questions below AND your answers and highlight/underline key words: 1. What is the product of the process of TRANSLATION? a) b) c) d) A complementary mRNA strand Increased production of ribosomes A completed protein Replacement of disabled nucleotides 2. A mutation is LEAST LIKELY to affect a cell when the mutation – a) Reverses the order of bases in a DNA strand b) Allows the total number of bases in a DNA sequence to remain the same c) Replaces a base with its complementary base d) Produces a codon that codes for the same amino acid as the original codon Cell division: the process in which a cell grows and divides into two identical daughter cells Cell Cycle : the series of events that cells go through to grow and divide. • Made up of two major phases: Interphase & M Phase • Used for organism growth and damage repair • Results in 2 identical cells G1 Phase S Phase G2 Phase Interphase: • Majority of a cell’s life • Includes 3 phases (G1, S, G2) G1: cell increases in size, makes new proteins and organelles. S phase: DNA is replicated (copied) Turn to your partner and discuss… WHY does the DNA have to replicate before the nucleus and cell divide? G2 Phase: the organelles and proteins required for cell division are produced. When the G2 phase is complete, the cell is ready to divide.