* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Baggie Cell Model Recommended Group Size
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
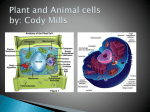
Grade: Activity #: Activity Title: Recommended Group Size: 4th 1 Baggie Cell Model Individual Purpose To construct a model that shows the parts of an animal cell. Cells are the building blocks of all living things. Equipment • • • • • • • • • • • • • (An asterisks (*) indicates that an item is provided in the Learning Lab.) Plastic Cups* Ziploc Sandwich Bags* Plastic Eggs* Green Yarn (3 each, 6 inches long)* White String (6 feet long)* Pipe Cleaners (2 each)* Toothpicks (5 each)* Kidney Beans (15 each)* Alaska Peas (20 each)* Colored Beads (20 each)* Sodium Polyacrylate* Water* Measuring Spoons and Cups* Instructions • • • Place the plastic bag (cell membrane) inside the plastic cup. Fold the edges of the plastic bag over and around the lip of the cup. Place the Alaska peas (lysosomes), kidney beans (mitochondria), toothpicks (microtubules) and green yarn (Golgi apparatus) inside the plastic bag in the cup. Take 10 of the colored beads (ribosomes) and thread them onto 1 pipe cleaner (endoplasmic reticulum). Space the beads apart evenly. Bend the pipe cleaner to resemble the shape of the ER by folding back and • • • • • • • • • forth. Place the bent pipe cleaner with colored beads (rough endoplasmic reticulum) inside the plastic bag in the cup. Bend the remaining pipe cleaner to resemble the shape of the ER. Place this bent pipe cleaner (smooth endoplasmic reticulum) inside the plastic bag in the cup. Place the remaining colored beads (ribosomes) inside the plastic bag in the cup. Add 1 teaspoon of sodium polyacrylate to the bag. Take the white string (DNA) and place it inside the plastic egg (nucleus). Close the plastic egg tightly and set it aside. Carefully add 6 oz of water to the bag in the cup. The sodium ployacrylate will swell in the presence of water to give a gel-like consistency. Place the plastic egg (nucleus containing DNA) inside the plastic bag in the cup. Carefully remove bag from cup, push air out and seal the bag. Gently massage the bottom of the bag to aid in gelling the water. Be careful not to puncture the bag. The gelled water represents the cytoplasm of the cell. You have created a model of an animal cell. Suggested Discussion Topics • • • The Cell is the basic unit of life on Earth. All living things are composed of cells. Living things might take the form of small, simple, unicellular organisms like bacteria, or the form of large, complex, multicellular organisms like pine trees and human. Generally speaking, the cells of complex, multicellular organisms are specialized cells. Each cell has a specific job and this job is reflected in the shape and structures of the cell itself. Specialized cells are organized into tissues, tissues into organs, and organs into complex organisms. Jobs of cell components and organelles: Cell Membrane - the thin layer of protein and fat that surrounds the cell. Provides the cell with its shape and structure. The cell membrane is semipermeable, allowing some substances to pass into the cell and blocking others. Cytoplasm – the jellylike material outside the cell nucleus in which the organelles are located. Nucleus – the control center of the cell. It is the place where hereditary information – the DNA- is located. DNA does not leave the nucleus. Instead, it sends messages out from the nucleus to the rest of the cell. Lysosome –round organelles surrounded by a membrane and containing digestive enzymes. They break down molecules in the cell. DNA – Deoxyribonucleic Acid, or DNA, is the cell’s hereditary material. It is arranged in a twisted ladder or “double helix” shape. A complete set of genetic instructions is present in the DNA of each cell. Ribosome – make proteins. They exist in the cell’s cytoplasm and associated with the endoplasmic reticulum. Mitochondria – can be considered the “power plants” of cells. They are responsible for converting glucose to energy. Golgi Apparatus – flattened, layered, sac-like organelle that looks like a stack of pancakes and is located near the nucleus. The Golgi apparatus packages proteins and carbohydrates into membrane-bound vesicles for “export” from the cell. Endoplasmic Reticulum – or ER, acts as a passageway for molecules in the cell to travel through. For this reason, its shape is long and ribbon-like. There are two types of ER: rough and smooth. Rough ER is covered with ribosomes, smooth is not. Microtubules – rod-like structures that help the cell maintain its shape. Vacuole – Fluid-filled, membrane-surrounded cavities inside a cell. The vacuole fills with food being digested and waste material that is on its way out of the cell. • • • Microscopes (There are “microscopes” in the yellow cases on the back shelf of the Learning Lab. There should be one for every student and there are plastic slides some of which have images of cells and their components) Similarities and differences of Plant and Animal Cells – How could you make your animal cell a plant cell? How could you compare a cell to a factory? Additional Resources http://www.carolina.com/text/teacherresources/instructions/miscbiology/baggie_cell_mod el.pdf http://www.carolina.com/category/teacher+resources/instructions+and+buying+guides/misc ellaneous+biology+instruction+manuals/baggie+cell+model.do http://www.biology4kids.com/files/cell_main.html http://www.neok12.com/Cell-Structures.htm http://www.kidsdiscover.com/cells-for-kids Adapted by Science Works from Carolina Biological