* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Osmosis/cell membrane - Duplin County Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Ethanol-induced non-lamellar phases in phospholipids wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
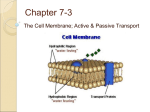
Cell Membranes Diffusion, Osmosis Tonicity Function of Plasma Membrane- Controls what enters and exits the cell. Also acts like a boarder, preventing cells internal environment from coming in contact with external environment. Fluid Mosaic Model The model, which was devised by SJ Singer and GL Nicolson in 1972, describes the cell membrane as a two-dimensional liquid in which phospholipid and protein molecules diffuse easily. Phospholipid Bilayer Hydrophilic Hydrophobic Phospholipid OUTSIDE Heads Tails Heads INSIDE 5 6 7 1 2 3 4 Cholesterol = adds to the fluidity of the phospholipids 5 6 7 3 4 Protein (Integral and Peripheral) Functions 5 6 7 Surface Carbohydrates (Glycoproteins and Glycolipids) = Function in cell recognition, cell signaling, and cell adhesion Diffusion- when molecules pass through a membrane. Osmosis – when water only passes through a membrane. Permeable- molecules pass through membrane. Impermeable – molecules can’t pass through membrane. Selective or Semi-permeable – membrane will allow certain size molecules to pass through. Cell Membrane’s Function? Controls what enters and exits the cell Selective Permeability = allows certain items to pass in/out What items pass easily? Small Uncharged (neutral) Transport Processes: Passive Transport -Diffusion (Simple and Facilitated) -Osmosis Active Transport Passive Transport = No energy required Concentration Gradient High Low = Reach +Equilibrium Diffusion molecules other than H2O ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ What else operates by Diffusion? Facilitated Diffusion = Diffusion through a protein (integral) What type of molecule? Large and/or charged Simple Diffusion Facilitated Diffusion Diffusion molecules other than H2O ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Osmosis water Passive Transport Active Transport Fig. 8.16 Both diffusion and facilitated diffusion are forms of passive transport of molecules down their concentration gradient, while active transport requires an investment of energy to move molecules against their concentration gradient. Active Transport Energy? Requires energy Concentration Gradient (with or against)? Why? HIGH LOW Would this be an example of (passive or active) transport? Sodium Potassium Pump (Na+ K+ pump) Passive Active Passive Why do you think they call the proteins in the plasma membrane the gatekeepers? Name some of the molecules that must enter and exit the cell on a daily, hourly, minute by minute bases. What is the cellular environment like? Surrounded by water ? ? 3 Types of “Solution”: • Isotonic Solution = solutions with equal solute concentrations • Hypotonic Solution = solution with the higher concentration of solutes • Hypertonic Solution = solution with the lower concentration of solutes “passive transport” Tonicity Animal Cells #1 #2 #3 Plant Cells Q. What kept the plant cell from bursting in picture #1? Isotonic Hypotonic Hypertonic Define Plasmolysis: occurs in a plant cell during a hypertonic situation, plasma membrane pulls away from cell wall due to shrinking of water vacuole. Isotonic Hypertonic (Plasmolysis) 1. 2. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What does the blue represent? (water or molecules of solute-salt) What do the purple dots represent? (water or molecules of solute) *count molecules on each side of membrane. Identify membrane, notice it’s location. What does selectively permeable membrane mean? Notice water level in start U-tube. Describe. Notice water levels in finished U-tube. Describe. Remember you are looking at concentration levels of WATER. On start U-tube which side has higher concentration of water. Go HL, what happens? 6. Which molecule was allowed to pass through the selectively permeable membrane? 7. Remember all membranes have pores they just vary in size. So which molecule is smaller (water or solute-purple dots). 8. Would the U-tube example represent (osmosis or diffusion)? Explain your answer. 9. Would the U-tube example represent (passive or active) transport of molecules? Explain your answer.