* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 1 Lesson 3 - Epiphany Catholic School
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
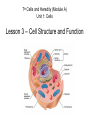
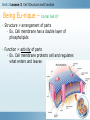
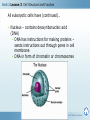
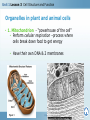
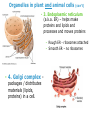
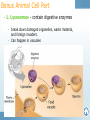
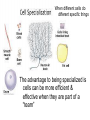
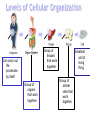
7th Cells and Heredity (Module A) Unit 1: Cells Lesson 3 – Cell Structure and Function Unit 1 Lesson 3 Cell Structure and Function Being Eu-nique – ha ha! Get it? • Structure = arrangement of parts • Ex. Cell membrane has a double layer of phospholipids • Function = activity of parts • Ex. Cell membrane protects cell and regulates what enters and leaves Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 3 Cell Structure and Function Characteristics of eukaryotic cells • All eukaryotic cells have… • Cell membrane (previous slide) • Membrane-bound organelles (next few slides) • Cytoplasm – fluid-like substance that fills cell contains • Cytoskeleton – network of protein filaments that give shape and support cell • Helps in cell division and movement • Found throughout cytoplasm Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 3 Cell Structure and Function All eukaryotic cells have (continued)… • Nucleus – contains deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) • DNA has instructions for making proteins – sends instructions out through pores in cell membrane • DNA in form of chromatin or chromosomes Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 3 Cell Structure and Function Organelles in plant and animal cells • 1. Mitochondrion - “powerhouse of the cell” • Perform cellular respiration –process where cells break down food to get energy • Have their own DNA & 2 membranes Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 3 Cell Structure and Function Organelles in plant and animal cells (con’t) • 2. Ribosomes - make proteins by putting together chains of amino acids • not enclosed in a membrane. • some are “free” others attached to endoplasmic reticulum. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Organelles in plant and animal cells (con’t) • 3. Endoplasmic reticulum (a.k.a. ER) – helps make proteins and lipids and processes and moves proteins • Rough ER - ribosomes attached • Smooth ER – no ribosomes • 4. Golgi complex packages / distributes materials (lipids, proteins) in a cell. •5. Vacuole – used for storage • In plants, may be large, filled with fluid, and used to support cell Animal cell Plant cell Let’s draw! Draw a cell with the following parts • Nucleus • Cytoskeleton • Cytoplasm • Nucleolus • Golgi complex • Mitochondria • Endoplasmic reticulum • Chromatin • Vacuole Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Bonus Plant Cell Parts • 1. cell wall-surrounds the cell membrane • Rigid - provides support and protection • Also in some fungi, archaea, bacteria, and protists 2. Chloroplast – where photosynthesis occurs Photosynthesis is the process by which cells use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to make sugar and oxygen Chloroplasts are green because of the green pigment chlorophyll (absorbs solar energy) Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 3 Cell Structure and Function What additional parts are found in plant cells? • How does a chloroplast make food for a plant cell? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Bonus Animal Cell Part • 1. Lysosomes - contain digestive enzymes • break down damaged organelles, waste material, and foreign invaders. • Can happen in vacuoles Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Your Misson • Use a ruler and a pencil to mark strips on a piece of paper that are 8 inches long and 1 inch wide • Use scissors to cut out each strip • Use a pen or pencil to write the entire alphabet on each strip • Make the first loop in the chain and tape it together • Now make a chain by threading the loops When different cells do different specific things The advantage to being specialized is cells can be more efficient & effective when they are part of a “team” Group of tissues that work together Can carry out life processes by itself Group of organs that work together Smallest unit of living thing Group of similar cells that work together Do unicellular organisms have levels of organization? NO! Only one cell to do all the things! Arrangement of parts How something works