* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 2: The Cell
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
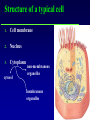
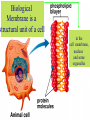
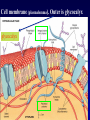
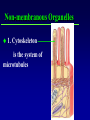
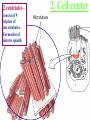
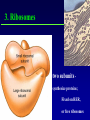
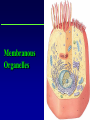
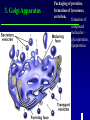
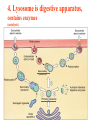
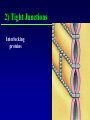
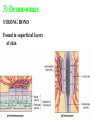
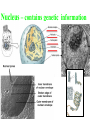
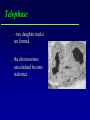
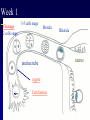
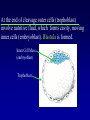
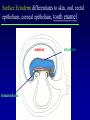
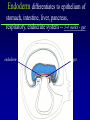
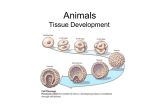
Kharkov National Medical University Department of Histology, cytology and embryology HISTOLOGY studies microscopic structure and function of the human organism is the structural and functional unit of the organism Structure of a typical cell 1. Cell membrane 2. Nucleus 3. Cytoplasm cytosol non-membranous organelles membranous organelles Biological membrane Biological Membrane is a structural unit of a cell in the cell membrane, nucleus and some organelles Cell membrane (plasmalemma). Outer is glycocalyx glycocalyx Non-membranous Organelles 1. Cytoskeleton is the system of microtubules 2 centrioles – consist of 9 triplets of microtubules. Formation of mitotic spindle 2. Cell center 3. Ribosomes two subunits synthesize proteins; Fixed on RER, or free ribosomes Membranous Organelles 1. Mitochondrion (two membranes) synthesis of energy - ATP 2. Endoplasmic reticulum (net of membranes) smooth (SER) & rough (RER) RER contains ribosomes SER Function: Synthesis Storage Transport SER of lipids and carbohydrates RER of proteins 3. Golgi Apparatus Packaging of proteins, formation of lysosomes, secretion, formation of compound molecules – glycoproteins, lipoproteins 4. Lysosome is digestive apparatus, contains enzymes (autolysis) Intercellular Junctions 1) Gap Junction has channel proteins 2) Tight Junctions Interlocking proteins 3) Desmosomes STRONG BOND Found in superficial layers of skin INCLUSIONS are nonliving components of a cell like: secretory granules, pigment, lipid, glycogen Nucleus – contains genetic information Cell Cycle _ _ _ The life of a somatic cell is a cyclic process - cell cycle consists of two periods: interphase and mitosis. interphase contains G 1, S, G 2 stages CELL CYCLE: Stages G1 Gap 1 growth, function S G2 M G1 Go DNA Synthesis (for new cells) stem Gap 2 formation of m.spindle, energy Mitosis or Gap 1 for a for new cycle differen tiation Mitosis _ Mitosis is the process of somatic cells division. _ Mitosis consists of : prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase. _ _ Prophase _ Chromosomes become more coiled and visible _ the nuclear membrane breaks down _ Microtubules of centrioles form a spindle of division. Ch Metaphase _ - chromosomes move to the center of the cell and form the equatorial plate Ch Anaphase _ - the chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles of the cell Ch Telophase _ - two daughter nuclei are formed. _ the chromosomes uncoiledand become indistinct. EMBRYOGENESIS IS FORMATION OF THE HUMAN ORGANISM Week 1 _ 1.Fertilization – is the fusion of the sperm and ovum = Zygote formation _ 2.Cleavage – is the division of the zygote in the uterine tube = Blastula formation Week 1 Cleavage 2 cells stage 3-5 cells stage Morula Blastula . . uterine tube zygote Fertilization uterus Implantation Day 6 - 8 At the end of cleavage outer cells (trophoblast) involve nutritive fluid, which forms cavity, moving inner cells (embryoblast). Blastula is formed. Inner Cell Mass (embryoblast) Trophoblast Week 2. 3.Early Gastrulation (division and movement of cells). At the beginning of gastrulation (6,7 day) germ sinks into the uterine wall – implantation. Gastrulation leads to formation of three germ layers – ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm and extraembryonic organs: amnion, yolk sac chorion Week 2 Ectoderm chorion amnion Endoderm yolk sac Extraembryonic Mesoderm of Amnion and Yolk Sac Gastrulation is finished with the formation of axial organs – neural tube, notochord, somites (mesoderm), locating between ectoderm and endoderm. From them develop tissues and organs! Neural tube Somate amnion ectoderm endoderm yolk sac Notochord 4. Body flexion (amnion increases and forms body) Body flexion formation (Gut formation. Gut is the upper part of yolk sac) longitudinally transversely gut head right left Differentiation of germ layers and axial organs _ What develops from them? Surface Ectoderm differentiates to skin, oral, rectal epithelium, corneal epithelium, tooth enamel amnion stomatodeum ectoderm Endoderm differentiates to epithelium of stomach, intestine, liver, pancreas, respiratory, endocrine system -- 3-4 weeks - gut endoderm gut Extra mesoderm- formation of the first blood vessels in the wall of yolk sac and allantois blood vessels Body Mesoderm urogenital system including kedneys, gonads, ducts, and accessory glands 3. Intermediate Mesoderm. Nephrotome dermatome - dermis of skin 1. Somitemyotome - muscles, sclerotome skeleton, except skull, 2. Lateral Mesoderm serous membranes of pleura, pericardium and peritoneum 4. Mesenchyme (loose part) – connective tissue of viscera and limbs, blood and lymph cells, vessels, smooth muscle Late embryonic stages _ _ Histogenesis Organogenesis