* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ETC Details
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
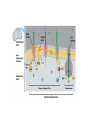
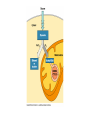
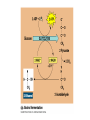
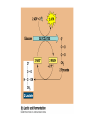
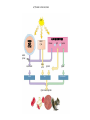
ETC Details • Electrons power proton pumps pump H+ out into intermembrane space • Generates ATP when H+ diffuse back into matrix thru ATP Synthase (Chemiosmosis) • NAD+ powers 3 pumps 3 ATP • FAD+ powers 2 pumps 2 ATP • http://www.nature.com/nrg/journal/v2/n5/animation/nrg0501_342a_swf_MEDIA1.html Bookkeeping Bookkeeping • NADH • • • • FADH • • Glycolysis Bridging Krebs Krebs ATP • • • Glycolysis Krebs ETC • • NADH X 3 = FADH X 2 = Fermentation • • • • Anaerobic Respiration No O2 required Plants Ethyl Alcohol Fermentation Animals Lactic Acid Fermentation • Produces: • 2 ATP (From glycolysis) • Ethyl alcohol • Lactic Acid Catabolism • Carbohydrates • Broken down into glucose • Starts at glycolysis • Proteins • Broken into amino acids, then converted into either pyruvic acid, acetyl CoA, or 1 of the molecules used in Krebs • Where it enters, depends on what’s made • Lipids • Splits into either glycerol or fatty acids (hydrocarbon tails) • Glycerol splits into G3P and enters glycolysis • Fatty acids undergo oxidation splits hydrocarbon tails and enter Krebs as acetyl CoA Anabolism • Aka Biosynthesis • How cells take molecules from food and turn them into molecules for growth and repair • Aka Metabolic Pool • Intermediaries of all cycles can be removed and used to build molecules! • Ex. pyruvate glucose • Acetyl CoA fatty acids ATP needed to drive biosynthesis ATP CITRIC ACID CYCLE GLUCOSE SYNTHESIS Acetyl CoA Pyruvate G3P Glucose Amino groups Amino acids Proteins Fatty acids Glycerol Fats Cells, tissues, organisms Sugars Carbohydrates Objectives • For each phase, know the following: • Input • Output - where it occurs - aerobic or anaerobic • What are the electron acceptors? • Given a molecule, be able to tell me whether it was oxidized or reduced • Compare and Contrast substrate level phosporylation and chemiosmosis • If you altered some part of the cell, how would it affect respiration? (ex. Mitochondria, membrane permeability to H+, blockage of proteins)