* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fill in the Captions AP Lesson #26 Are our diets only glucose? How
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
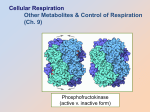
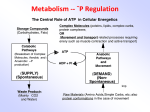
Fill in the Captions AP Lesson #26 EQ: How does metabolism utilize other organic compounds and regulate cellular respiration? 2 2 ~32 Are our diets only glucose? How do we get energy from other carbs? • Glycolysis accepts a wide range of carbohydrates fuels polysaccharides → → → glucose hydrolysis • ex. starch, glycogen other 6C sugars → → → glucose Modified by enzymes • ex. galactose, fructose How can we get energy from Proteins? proteins → → → → → amino acids How do we get energy from lipids? fats → → → → → glycerol + fatty acids hydrolysis hydrolysis glycerol (3C) → → G3P → → glycolysis waste H O H | || N —C— C—OH | H R amino group = waste product excreted as ammonia, urea, or uric acid fatty acids → 2C acetyl → Acetyl → Krebs groups CoA Cycle glycolysis Krebs cycle 2C sugar = carbon skeleton = enters glycolysis or Krebs cycle at different stages 3C glycerol enters glycolysis as G3P 2C fatty acids enter Krebs cycle as acetyl CoA 1 Which has more energy, carbs or fats? • Coordination of chemical processes across whole organism • Fat generates 2x ATP vs. carbohydrate – more C in gram of fat • more energy releasing bonds • takes longer to digest = slower release of energy – digestion • catabolism when organism needs energy or needs raw materials – more O in gram of carbohydrate • so it’s already partly oxidized • less energy to release What is metabolism? – synthesis • anabolism when organism has enough energy & a supply of raw materials fat carbohydrate – by regulating enzymes CO2 • feedback mechanisms • raw materials stimulate production • products inhibit further production What role does digestion play in metabolism ? What role does synthesis play in metabolism ? • enough energy? build stuff! • cell uses points in glycolysis & Krebs cycle as links to pathways for synthesis • Digestion – run pathways “backwards” • have extra fuel, build fat! CO2 pyruvate → → glucose Krebs cycle intermediaries acetyl CoA Remember Feedback Inhibition • Regulation & coordination of production – final product is allosteric inhibitor of earlier step – no unnecessary accumulation of product – production is self-limiting → X 1 → A→B→C→D→E→F→G → – ATP is only good as short term energy – Feedback inhibition → → fatty acids → • Feedback Control amino acids → How do we make sure that we don’t have ATP just hanging around? →→ → – Catabolism of carbohydrates, fats & proteins • all break down through same pathways • enter at different points as intermediates – cell extracts energy from every source 2 3 4 5 6 enzyme enzyme enzyme enzyme enzyme enzyme allosteric inhibitor of enzyme 1 2 How is metabolism similar to an economy in living things? How is ATP production regulated? • Phosphofructokinase • Basic principles of supply & demand regulate metabolic economy – allosteric regulation of this enzyme • why here? “can’t turn back” step before splitting glucose – balance the supply of raw materials with the products produced – these molecules become feedback regulators • they control enzymes at strategic points in glycolysis & Krebs cycle – AMP & ADP stimulate – ATP inhibits – citrate inhibits • Balancing synthesis with availability of both energy & raw materials is essential for survival! Why is this regulation important? Balancing act: availability of raw materials vs. energy demands vs. synthesis Summarizing Strategy • Acrostic – Cell Respiration C E L L – a short phrase or sentence that begins with each letter of the vertical word and offers important information or key characteristics about the topic. Assessment HW: Complete Case Study #3 R E S P I R A T I O N Fill in the Captions 2 2 ~32 Fill in the Captions 2 2 ~32 3