* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3 Nucleosides nucleotides and nucleic acids
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
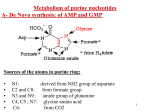
This document was created by Alex Yartsev ([email protected]); if I have used your data or images and forgot to reference you, please email me. Nucleotides, Nucleosides and Nucleic Acids NUCLEOSIDES These are sugars which are linked to a nitrogen containing base. Those of interest are PURINES and PYRIMIDINES, which have ring structures. The NUCLEOSIDE is complete when a purine or a pyrimidine binds to ribose or 2deoxyribose. Eg. Adenine (a nucleotide) forms Adenosine when bound to ribose. NUCLEIC ACIDS These are dietary organic acids which get digested and broken down into compenent purines and pyrimidines. Most purines and pyrimidines however are synthesized de novo from amino acids, mainly in the liver. RNA is constantly recycled, but DNA is stable throughout your lifespan NUCLEOTIDES The above purine and pyrimidine ring structures, with the addition of inorganic phosphate, are called NUCLEOTIDES. PURINE NUCLEOTIDES: Adenine and Guanine PYRIMIDINE NUCLEOTIDES: Cytosine, Thymine, Uracil PYRIMIDINE and PURINE CATABOLISM PYRIMIDINES Beta- Amino acids Because Beta-aminoisobutyrate is a urine-excreted product of thymine catabolism, it can be used to measure DNA turnover Beta-Alanine Further degradation Beta-aminoisobutyrate CO2 NH3 PURINES: Adenosine Hypoxanthine Xanthine Oxidase Guanosine ALLOPURINOL Xanthine Inhibits this step Xanthine Oxidase URIC ACID EXCRETION Usually the level is about 0.24 mmol/L URIC ACID IN THE KIDNEY: - 90% of urate is reabsorbed - 2% of urate is not reabsorbed - 8% of urate is SECRETED actively in the tubules On a normal diet, you excrete about 1 gram per day DNA, Deoxyribonucleic acid This document was created by Alex Yartsev ([email protected]); if I have used your data or images and forgot to reference you, please email me. Extremely long nucleotide chains containing - ADENINE - GUANINE - THYMINE - CYTOSINE The double helix is held together by hudrogen bonds between the bases : - ADENINE BONDS TO THYMINE - GUANINE BONDS TO CYTOSINE A diploid human cell contains 46 chromosomes. Useful factoid to know. - EXONS are portions of genes which encode protens; - INTRONS are portions of the gene which are not encoded into proteins - PROMOTER regions are near the transcription start of the gene, and this is where RNA polymerase binds to start the encryption of RNA; it usually includes a TATA (thymine-adenine-thymine-adenine) sequence - There are also REGULATORY sequences along the gene (about 5 of them) which are ENHANCERS and PROMOTERS MITOSIS and MEIOSIS - Each time the cell divides, it follows a sequence of steps, as below: - FIRST, DNA polymerase catalysis the separation of the double helix into two chains The INTERPHASE: everything that isn’t mitosis (M phase) - o G1 = “gap” phase, period of cell growth which follows division; centrioles replicate o S phase = DNA replicates o G2 phase = final growth and ativity before mitosis Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis follow – the M phase PLOIDY: - The number of chromosomes in a cell DIPLOID: normal resting “euploid” cells with the normal number of chromosomes. TETRAPLOID is what normal diploid euploid cells become at the point where they are about to divide ANEUPLOIDY is an abnormal number of chromosomes, commonly found in cancerous cells RNA, Ribonucleic acid - SINGLE-STRANDED HAS URACIL INSTEAD OF THYMINE The production of RNA from DNA is called TRANSCRIPTION Transcription is mediated by RNA Polymerase Most forms of RNA are involved in TRANSLATION which is the formation of proteins from the genetic code The translation process occurs in ribosomes References: Ganong's Review of Medical Physiology, Chapter 1