* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download study guide - Dorman High School
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
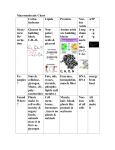
STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER 2: CHEMISTRY OF LIFE 1. Given a structural diagram, identify the following types of molecules: a. carbohydrate (mono-, di-, and polysaccharide) b. protein (amino acid, polypeptide, dipeptide) c. lipid (glycerol, fatty acid, triglyceride, phospholipid, steroid) d. nucleic acid (DNA, RNA, purines, pyrimidines, ribose, deoxyribose) e. ATP 2. Given a structural diagram, identify the following: a. amine group b. carboxyl group c. peptide bond d. saturated fat vs. unsaturated fat 3. Tell the difference between organic and inorganic compounds. 4. Describe why water is a polar molecule. 5. Explain the following properties of water with regard to the human body: a. high specific heat b. high heat of vaporization c. solvent 6. Define acid, base, and salt. 7. Discuss pH with regard to normal human pH and pH values for acids and bases. 8. Contrast acidosis and alkalosis. 9. Describe the role of buffers in the body. 10. Name the reactants and products in a neutralization reaction. 11.Name 3 hexoses and give their source. 12. Name 2 pentoses and give their source. 13. Tell the chemical difference between ribose and deoxyribose. 14. Name 3 disaccharides and tell which 2 monosaccharides form each. Also tell where you can find each of the disaccharides. 15.Name 3 polysaccharides and where they can be found. 16. Describe how polysaccharides, polypeptides, and triglycerides are formed and broken down. 17.Name the “building blocks” of proteins and tell how types of them there are. 18.Explain the four levels of protein structure. 19.Differentiate between the alpha helix proteins and the beta pleated sheet proteins (structure and function). 20.Give examples of globular and structural proteins. 21.Define “denature” with regard to proteins and tell how it can happen. 22.Name 3 classes of lipids and describe their general functions. 23.What are the building blocks of a triglyceride, phospholipid, and steroid? 24.Which class of compounds contains DNA and RNA? 25.What is the purpose of the nucleic acids? 25.Name the 3 parts of a nucleotide. 26.Tell which nitrogenous bases are purines and pyrimidines. 27.Tell which bases pair with each other (complementary base pairing, i.e. A with T (or U in RNA) and G with C). 28. What is the “energy currency” of the body (the molecule that captures, stores, and releases energy)? 29. What is it about ATP that allows it to store so much energy? 30. What three molecules make up ATP? 31. What is an electrolyte and what is its purpose in the body? 32. Know vocabulary and stems. Essay possibilities: 1. Describe the four levels of protein structure. 2. Draw and describe the structure of a cell membrane, showing how phospholipids work to form the phospholipid bilayer. 3. Discuss why maintaining a normal pH is so critical in the human body and recognize acidosis and alkalosis.