* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Biological aspects of fluorine wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
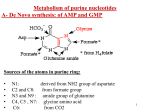
Metabolism of purine nucleotides A- De Novo synthesis: of AMP and GMP Sources of the atoms in purine ring: • • • • • N1: derived from NH2 group of aspartate C2 and C8: from formate group N3 and N9 : amide group of glutamine C4, C5 , N7: glycine amino acid C6: from CO2 1 2 Notes on purine nucleotides biosynthesis: 1. Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) is the source of ribose 5-phosphate. Pyrophosphate is removed. 3 2- The ring is then formed from their atoms sources (aspartic, glutamine, glycine, etc). 3- PRPP is an activator to pathway i.e, increased PRPP leads to overproduction of purine nucleotides 4- The pathway ends with the formation of a purine nucleotide called : Inosine monophosphate (IMP) which is the precursor of AMP and GMP which then converted into ATP and GTP, respectively AMP and GMP ← 4 NB: IMP is a nucleotide contain purine base which is hypoxanthine (6 –oxy purine). Hypoxanthine is a purine base not enter in DNA or RNA structure hypoxanthine 5 Catabolism ( breakdown) of purine nucleotides Synthesis of uric acid: Uric acid is the end product of purine metabolism in human. AMP or GMP is metabolized to give hypoxanthine which is then converted into xanthine and finally into uric acid as in the next slide. Most of uric acid is excreted by the kidney. The remaining uric acid travels through the intestines, where bacteria help break it down. Normally these actions keep the level of uric acid in the blood plasma at a healthy level, which is below 6.8 mg/dL. But under certain circumstances, the body produces too much uric acid or removes too little. In either case, concentrations of uric acid increase in the blood. This condition is known as hyperuricemia. 6 7 Gout: is a disorder characterized by high levels of uric acid in blood (hyperuricemia), with deposition of monosodium urate crystals in special sites in the body like joints, and surrounding tissues and sometimes in the kidney. Gout is a type of arthritis Urate crystals are detected in synovial fluid of the joint 8 Causes: 1- decreased excretion of uric acid by the kidney due to renal disease, acidic urine that decrease uric acid excretion, some drugs inhibit uric acid excretion such as thiazide diuretics. Sometimes it is inherent. 2- Diet rich in purines such as red meat, duck, liver, xanthine beverages like tea, coffee, cola. 3-Overproduction of uric acid due to increased synthesis of purine nucleotides which may be idiopathic (with unknown cause) or due to increased levels of PRPP that stimulate synthetic pathway of purine nucleotides. Symptoms: 1- Hyperuricemia: increased uric acid levels in blood 2- arthritis, inflammation especially in joints due to deposition of urate crystals leading to hot red and swollen joints with severe pain. 3- redness, swelling of big toe. 9 4- it may also present as tophi (masses of urate crystals deposited under skin) appears after several years. 5- It may lead to kidney stones, Tophi, in chronic cases, lumpy deposits of urate just under the skin 10 Treatment: Allopurinol, analogue of hypoxanthine (structurally similar). It competitively inhibits xanthine oxidase, so prevents the conversion of hypoxanthine to xanthine and xanthine to uric acid. Uricosuric agents: drugs used to increase excretion of uric acid by the kidney such as probenecid. 11 Anti-inflammatory drugs is recommended also. 12 Pyrimidine metabolism Sources of carbon and nitrogen atoms in pyrimidine ring: N1, C4, C5 and C6 → from aspartate C2 from CO2 N3 → from amide group of glutamine 13 De no vo biosynthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides (UTP, CTP): • pyrimidine nucleotides are synthesized by a stepwise series of reactions to form UMP. • Pyrimidine ring is formed first then ribose-5- phosphate is added via PRPP. • NB. In purine synthesis, ribose-5-P is added from the first step, then, the ring is formed. • The rate limiting step in de novo synthesis of pyrimidine is the first step which is the formation of cabamoyl phosphate from glutamine and CO2 in the presence of 2ATP and carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II which is the rate limiting enzyme. 14 Pyrimidine Catabolism 1- Ring Cleavage: pyrimidine ring can be opened and degraded to highly soluble βamino acids such as β- alanine and β-aminoisobutyrate 15 Some Functions of nucleotides: 1- Enter in the structure of DNA and RNA. 2- ATP and GTP are sources of energy 3- CTP is required for synthesis of phosphlipids that enter in the structure of cell membrane 4- enter in the synthesis of some coenzymes such as NAD, FAD, FMN. 16