* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5.1 The Cell Cycle
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
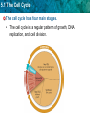
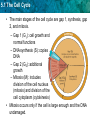
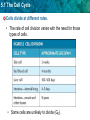
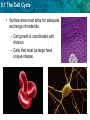
5.1 The Cell Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. 5.1 The Cell Cycle Objectives • Describe the stages of the cell cycle. • Compare rates of division in different cell types. • Identify factors that limit cell size. 5.1 The Cell Cycle Vocabulary • Cell Cycle – Pattern growth, DNA replication, and cell division that occurs in a eukaryotic cell. • Mitosis – Process by which a cell divides it nucleus and contents. • Cytokinesis – Process by which the cell cytoplasm divides. 5.1 The Cell Cycle The cell cycle has four main stages. • The cell cycle is a regular pattern of growth, DNA replication, and cell division. 5.1 The Cell Cycle • The main stages of the cell cycle are gap 1, synthesis, gap 2, and mitosis. – Gap 1 (G1): cell growth and normal functions – DNA synthesis (S): copies DNA – Gap 2 (G2): additional growth – Mitosis (M): includes division of the cell nucleus (mitosis) and division of the cell cytoplasm (cytokinesis) • Mitosis occurs only if the cell is large enough and the DNA undamaged. 5.1 The Cell Cycle Cells divide at different rates. • The rate of cell division varies with the need for those types of cells. • Some cells are unlikely to divide (G0). 5.1 The Cell Cycle Cell size is limited. • Volume increases faster than surface area. 5.1 The Cell Cycle • Surface area must allow for adequate exchange of materials. – Cell growth is coordinated with division. – Cells that must be large have unique shapes. 5.1 The Cell Cycle Question/Answer • What are the four main stages of the cell cycle? – Gap 1, synthesis, Gap 2, mitosis • What can you infer about the relative amount of time a cell spends in each stage? – An actively dividing cell spends the least amount of time in the mitosis stage. The length of Gap 1 varies the most and is usually the longest. • Do you think a skin cell would have a long or short G1 stage? Explain why. – A skin cell would probably have a short G1. Skin cells undergo a lot of wear and tear because they are exposed on the outside of the body. Therefore, they are probably replaced quickly. 5.1 The Cell Cycle Question/Answer • Which has the larger ratio of surface area to volume, a tennis ball or a soccer ball? Explain your reasoning. – A tennis ball, because volume increases more rapidly than does surface area as a ball gets larger.