* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Organelles
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
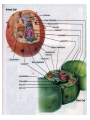
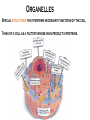
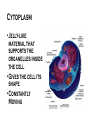
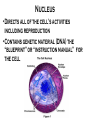
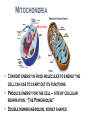
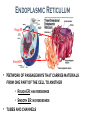
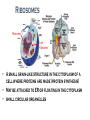
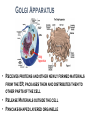
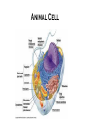
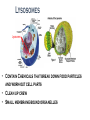
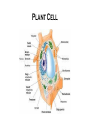
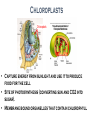
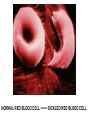
Where does life come from? • I can develop and use a model to describe the function of a cell as a whole and the ways the different parts of cells contribute to the function What are cell organelles? Organelles Special structures that perform necessary functions of the cell Think of a cell as a factory whose main product is proteins. The Cell Membrane • Controls movements into and out of the cell • Everything the cell needs enters through cell membrane • All cells have membranes • Is made of a phospholipid bilayer. Cytoplasm • Jelly-like material that supports the organelles inside the cell • Gives the cell its shape • Constantly Moving Nucleus • Directs all of the cell’s activities including reproduction • Contains genetic material (DNA) the “blueprint” or “instruction manual” for the cell Mitochondria Mitochondria • Convert energy in food molecules to energy the cell can use to carry out its functions • Produce energy for the cell – site of cellular respiration. “The Powerhouse” • Double membrane-bound, kidney shaped. Mitochondria Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough ER Smooth ER • Network of passageways that carries materials from one part of the cell to another • Rough ER: has ribosomes • Smooth ER: no ribosomes • tubes and channels Electron micrograph of smooth endoplasmic reticulum Rough endoplasmic reticulum with ribosomes Ribosomes Ribosomes Free Ribosomes • A small grain-like structure in the cytoplasm of a cell where proteins are made (protein synthesis) • May be attached to ER or floating in the cytoplasm • small circular organelles Golgi Apparatus Golgi Apparatus • Receives proteins and other newly formed materials from the ER, packages them and distributes them to other parts of the cell • Release Materials outside the cell • Pancake-shaped layered organelle Golgi Apparatus Vacuoles • Stores water, food, waste products and other materials for the cell • Plays a role in intercellular digestion • Are much larger in plant cells. What is the difference between an animal cell and a plant cell? Plant vs Animal Cells Plant and animal cells have a lot of the same organelles. Animal Cell Lysosomes Lysosomes • Contain Chemicals that break down food particles and worn-out cell parts • Clean up crew • Small membrane-bound organelles Plant Cell Cell Wall Cell Wall • Rigid layer of non-living material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms • Provides support and protection to the cell • Made of cellulose Chloroplasts Chloroplasts • Capture energy from sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell • Site of photosynthesis (converting sun and CO2 into sugar). • Membrane bound organelles that contain chlorophyll Plant Cell Small green chloroplasts can be seen inside each plant cell cork cells Pollen grains bone cells growth plate onion cells human red blood cells bacteria Brain cells Neuromuscular junction – where nerve cells connect with muscle cells moss cells Sperm and egg - conception blood clot Hair cells in inner ear rods and cones – cells of retina tooth plaque – bacteria + food particles basal cell carcinoma – skin cancer brain cells normal red blood cell ---------- sickled red blood cell common cold virus human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) H1N1 virus (swine flu)