* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fluid Mosaic Model
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
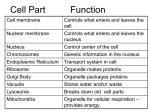
Cell Theory & The Scientists Involved Robert Hooke Cork oak (Quercus suber) Anton Van Leeuwenhock • Date: 1600’s • Theory: saw living organisms in pond water never seen before (animalcules). • Occupation: invented the simple microscope (single lens) Cell Theory • Cells are the structural units of all living things. (Cells carry on their own life functions) • New cells can only arise from other cells by the process of cell division • Viruses are not made up of cells. • Also viruses do not carry out there own life functions. • Where did the first cells come from? • Mitochondria and chloroplasts contain their own DNA. • Slime molds are multinucleated. I’m the Herpes Virus We’re Influenza Viruses! • Slime molds do not have cells as a basic unit. They have an unorganized cytoplasm and many nuclei, they also do not have a distinct cell shape Organelle • A specialized structure in the cytoplasm of a cell that carries out a specific function. Nucleus • Located in the center of a cell, the nucleus is a large, dense, membrane-enclosed body that controls the cell’s metabolism and reproduction. Nucleolus • Site of RNA (ribonucleic acid) production • A dense, granular body found in the nucleus Cell membranes are semi-permeable. This means that the cell membrane only allows certain substances to pass through it. (Phospholipid bilayer) Large structure comprised of smaller subunits. According to the Fluid Mosaic Model the cell membrane Is a two layered structure composed of lipids and proteins. And is what we currently believe the cell membrane is composed of. A hairlike organelle on the surface of a cell with the capacity for movement Green arrows point to Cilia Flagella • Involved in cell movement • Only a few on the cell surface • Whip-like tail • 9 microtubule doublets arranged in pairs • 2 microtubules in center Phagocytosis • The process in which large particles or small organisms are ingested into a cell. Pinocytosis The process in which liquids or very small particles are taken into a cell. The substance is in contact with the surface of the cell membrane, the membrane pinches and forms a pouch. Cytoplasm • A watery material located between the cell membrane and the nucleus. • Holds the organelles Endoplasmic Reticulum • A system of fluid filled canals or channels enclosed by membranes • Serve as a path of transport throughout the cell • Rough endoplasmic reticulum are lined by ribosomes. Ribosome • An organelle that is the site of protein synthesis in a cell. • They are produced by the nucleolus. Golgi Body • Serve as packaging and storing centers for the secretory products of the cell Lysosome • Small, saclike structures surrounded by a single membrane • Involved in the digestion of food within the food vacuoles of the cell • Found in white blood cells, in multicellular organisms Mitochondrion The powerhouse of the cell. An oval, membrane enclosed organelle, in which most of the reactions of cellular respiration occur. Mitochondrion Microfilament A solid, thread-like organelle that can function as a supporting structure or aid in cell movement. Act as “cross-bracing” in the cell. Microtubules • A long, cylindrical organelle found in cilia and flagella • Are also involved in the movement of the chromosomes during cell division • Composed of a protein called tubulin Vacuole • A fluid-filled organelle enclosed by a membrane. • Stores waste and food. • Occupies most of the space in the cytoplasm. Specialized vacuoles include… Contractile Vacuole • Extra water in the cell collects here and is expelled from the vacuole directly into the environment • Works kind of like a water pump Centrioles –found only in animal cells, these organelles aid in cell division. In addition to the organelles previously mentioned, plants also have additional organelles- Contain a cell wall Have chloroplasts Chloroplasts • A membrane-enclosed organelle found in the cells of some protists and almost all plants. • They capture the sun’s energy and convert it into chemical energy during the process of photosynthesis. Similarities – Plant and Animal Cells Both Have: A proper nucleus Cytoplasm A cell membrane Chromosomes Mitochondria Animals Do not contain a cell wall Do not contain chloroplasts Have small vacuoles Generally have spherical shape. Contain centrioles