* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells and Cell Theory PowerPoint
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
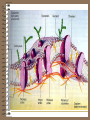
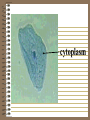
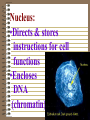
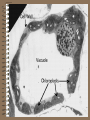
CELLS AND CELL THEORY CELL SCIENTISTS Robert Hooke-1665, observed small cavities in cork which he called cells. Anton van Leeuwenhoeklate 1600’s, refined the microscope; saw single-celled organisms which he called “animalcules” Rene Dutrochet-1824, discovered osmosis; concluded that plants and animals are both made of cells. Robert Brown-1831, First to see and name the nucleus Felix Dujardin-1835, first to notice cytoplasm Matthias Schleiden-1839, wrote a paper stating all plants are made of cells Theodor Schwann-1839, wrote a paper stating all animals are made of cells. Rudolf Virchow-1855, first to see cell division CELL THEORY: •All living things are made of cells •Cells are structurally and functionally similar •Cells come from other cells WHAT IS A CELL? The smallest unit that can perform all life processes. What is an Organelle? •one of several specialized structures, suspended in the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell. Prokaryotic Cells: 1. No nucleus 2. No membrane-bound organelles 3. Very small 4. DNA in one loop 5. Only bacteria Eukaryotic Cells: 1. DNA in long strands (chromatin) in nucleus 2. Large in comparison to bacteria (prokaryotes) 3. Many membrane-bound organelles 4. All other organisms, except bacteria EUKARYOTIC CELL STRUCTURE: CELL MEMBRANEEncloses all parts of the cell; Controls what goes in and out Cell Membrane Structure: •Phospholipid bilayer •Embedded with proteins: (Marker, Channel, Receptor) •Glycolipids •Glycoproteins •Fluid Mosaic Model Cell Wall: •Found in plants •Made of cellulose •Surrounds cell membrane •Provides rigidity for plant CELL WALL Cytoplasm: •Jelly-like substance in a cell •Surrounds other cell parts •Composed of water, salt, & other organic molecules cytoplasm Nucleus: •Directs & stores instructions for cell functions •Encloses DNA (chromatin) Nuclear Membrane • Double membrane that isolates the interior of the nucleus from the cytoplasm • Has pores to allow things to be transported into and out of the nucleus. • 4 phospholipid layers Nucleolus: •Inside of nucleus •Assembles ribosomes •May be 1 or more than 1 nucleolus Chromatin: •Long strands of a DNAprotein complex found in nucleus chromatin Nucleoplasm: •A viscous fluid in the nucleus in which the chromatin & nucleolus are suspended. Ribosomes: •Protein factories of cell •Line up amino acids in correct order ribosomes Mitochondria: •“Powerhouses” of cell •Make ATP •Complete breaking down of glucose molecules Golgi Apparatus: •Packages & distributes organic molecules that leave the cell •Surround molecules with membrane Lysosomes: Bags of enzymes that: •Digest macromolecules •Digest worn out cell parts •Destroy invading bacteria Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): •Membrane system of folded sacs & tunnels •Helps maintain homeostasis •Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): •Rough ER has ribosomes & transports proteins •Smooth ER has no ribosomes & transports lipid & carbs. •Attached to nucleus Centrioles & Centrosomes: •Organizing centers for cell division •Found only in animal cells centrioles centrosome PLASTIDS: A class of organelles found only in plants and in some protists. Chloroplasts: •Site where glucose is made •Contain chlorophyll Leucoplasts: •Change glucose to starch •Look like grains of rice •Starch is stored here leucoplast •Manufacture & store plant pigments •Red, orange, purple, yellow •Found in fruit, flowers & colorful leaves Vacuoles: •Fluid filled sacs •Store enzymes, water, and waste products •Large, central vacuole in plants •Many small vacuoles in other cells (or none at all) CYTOSKELETON: •Helps cell hold its shape •Made of microtubules and microfilaments •Animal cell rely on this for maintaining cell structure Microtubules: •Hollow rods of protein •Some extend from the cytoplasm to make up cilia and flagella Microfilaments: •Threadlike fibers found below the cell membrane •Produce flowing motion in cytoplasm •Help circulate organelles; improve cell efficiency Comparison of Plant Cells to Animal Cells: PLANT Cell Wall Plastids Large Vacuole Rely on cell wall for structure No centrioles ANIMAL No Cell Wall No Plastids Small vacuoles or none Rely on cytoskeleton Centrioles