* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bio 263/F94/T2 - millersville.edu
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
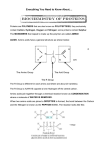
Biology 263 Cell Biology Joel Piperberg March 19, 2010 Second Exam Page # 1 Name ___________________________________ I. Multiple Choice. Fill in the circle on the test form corresponding to the correct answer. For the next six questions you will need to refer to the structures of the amino acid R groups shown at the end of the multiple choice questions. 1. ________ typically forms ________ bonds between two different protein subunits? a. Cysteine, covalent c. Cytosine, disulfide e. a and d b. Glycine, H d. Methionine, disulfide 2. Which of the tripeptides below would be least soluble in a hydrophobic solvent like benzene? a. N - phenylalanine - cysteine - glycine - C d. N - leucine - aspartate - glycine - C b. N - proline - phenylalanine - leucine - C e. N - arginine - proline - alanine - C c. N - glutamate - aspartate - lysine - C 3. Which of the amino acids listed below would be most likely to be found only on the interior of a polypeptide that has already adopted its active conformation and is in contact with the center of a lipid bilayer? a. phenylalanine b. c and e c. aspartate d. leucine e. glutamate 4. Which amino acid would be likely to have a charge of -1 at physiological pH 7.4? a. arginine b. lysine c. aspartate d. leucine e. a and b 5. Which amino acid would probably be found in the exterior of a protein in the cytoplasm? a. aspartate b. methionine c. lysine d. a and c e. all of the other answers 6. Which amino acid has a positive charge at physiological pH? a. methionine b. glutamate c. arginine d. b and c e. none of the above 7. What protein structure involves interaction between two portions of the same chain in the form of H bonds perpendicular to the axis of the molecule? a. -helix b. secondary c. a and b d. -pleated sheet e. b and d 8. Which of the following may occur if an amino acid in the middle of an -helix is changed from a helix-indifferent to a helix breaking amino acid? a. The helix is strengthened. c. The helix ceases to exist. e. c and d b. The helix becomes a -pleated sheet. d. The protein's function is lost. 9. Non-denaturing gel electrophoresis has the advantage that it ________________. a. c and e b. allows the detection of proteins in a gel by their biological activity c. separates on the basis of more than one property thus to some degree confusing the results d. separates solely on the basis of molecular weight e. separates on the basis of molecular weight and charge 10. A protein applied to a gel moves steadily down the gel and stops before reaching the end while the current is still on. Why did the protein stop moving? a. Its charge became positive. c. It was isometrically affected. e. It is denatured. b. Its charge became negative. d. Its charge becomes neutral. 11. What kind of polypeptide structure involves interaction within the same chains in the form of H bonds perpendicular to the axis of the molecule? Biology 263 Joel Piperberg Second Exam Name ___________________________________ a. primary b. secondary c. tertiary Cell Biology March 19, 2010 Page # 2 d. -helix e. b and d 12. Which technique effectively separates proteins on the basis of their size, shape and density and also on the basis of the medium through which they are moving? a. ion exchange chromatography c. non-denaturing gels e. SDS-PAGE b. sucrose density gradient centrifugation d. a and b 13. The final protein conformation (the 3-D shape) is ultimately determined by _________. a. the interaction between the R groups within the nucleic acid backbone b. interaction between sphingolipid R groups c. the interaction between adjacent or nearly adjacent regions of the carbohydrate backbone d. the primary structure e. all of the above 14. Which property below is typical of helical structure? a. a high degree of extensibility b. flexibility c. strength d. rigidity 15. Nucleation is most closely associated with which phenomenon below? a. renaturation b. protein folding c. transcription d. translation e. b and c e. a and b 16. What bonds are involved in holding together tertiary structure in proteins? a. disulfide linkages c. H bonds e. a and c b. hydronomic interactions d. peptide bond interactions 17. A protein you wish to study is located in the mitochondria of rat liver cells and is readily extractable from partially purified mitochondria. It has a highly negative charge at pH 7. You propose to use a series of techniques to purify the protein. In what order would you use the techniques after you had homogenized the tissue? a. sucrose density gradient centrifugation (SDGF)- extraction - isoelectric focussing (IEF) precipitation by ammonium sulfate b. differential centrifugation - SDGF - extraction - ammonium sulfate precipitation - CM (carboxymethyl) cellulose chromatography - affinity chromatography c. ammonium sulfate precipitation - SDGF - extraction - CM cellulose chromatography - IEF - SDGF d. IEF - affinity chromatography - differential centrifugation - extraction e. differential centrifugation- SDGF - extraction - ammonium sulfate precipitation - DEAE (diethylaminoethyl) cellulose chromatography - affinity chromatography 18. The Unit Membrane model was shown to be inaccurate because __________. a. all membranes were not exactly alike d. membranes vary in cholesterol content b. membranes are made up of phospholipids e. a, c and d c. membranes have different protein and lipid content 19. A protein is associated with the cell membrane and fully exposed to the extracellular environment of the cell. It can, however, be freed from the membrane by washing the cell with a low ionic strength salt solution. It is a ________ protein. a. peripheral b. extrinsic c. lipid-anchored d. transmembrane e. a and b 20. Resonance explains the ______ of the _______ bond that restricts the ability of a polypeptide to coil? a. extensibility, peptide c. high rotational freedom, peptide e. a and d Biology 263 Joel Piperberg Second Exam Name ___________________________________ b. rigidity, phosphate ester d. rigidity, peptide Cell Biology March 19, 2010 Page # 3 21. If there are only different 20 amino acids inserted into proteins, how do amino acids, which are not among the twenty (like hydroxylysine and hydroxyproline), get into proteins? a. They are added after synthesis. d. There really are 22 amino acids. b. They are present before synthesis. e. none of the above c. Amino acids inserted during synthesis are altered later. 22. Which technique could be used for molecular weight determinations in proteins under all circumstances? a. gel filtration d. a and e b. isoelectric focusing e. SDS-PAGE c. carboxymethyl (CM) cellulose chromatography 23. What is the lowest level of polypeptide structure in a protein exhibiting subunit structure? a. quaternary b. secondary c. tertiary d. -helix e. primary 24. You are purifying a protein. Before you have employed any procedures to purify it, its specific activity is 300 units/mg protein. After 5 successive purification procedures, the specific activity is 12,000,000 units/mg protein How much have you purified the protein? a. 40,000 times b. 4,000 times c. 400,000 times d. 0.00004 times e. .0004 times 25. What property of a protein can be determined directly with gel filtration chromatography if the protein is an oblate spheroid (cigar-shaped)? a. molecular charge b. molecular weight c. molecular shape d. Stokes' radius e. b and d 26. If a solution containing the following tripeptides were passed through a column packed with CMcellulose at pH 7, which of them would bind most effectively to the CM-cellulose column? (see drawing at end of Multiple Choice section for R groups) a. N - arginine - lysine - proline - C d. N - leucine - alanine - glycine - C b. N - aspartate - glutamate - aspartate - C e. N - aspartate - phenylalanine - leucine - C c. N - phenylalanine - aspartate - glycine - C 27. Which technique would be least likely to result in a high degree of purification? a. differential centrifugation c. precipitation e. affinity chromatography b. ion exchange chromatography d. homogenization 28. Which technique would be used to detect the differences in conformation seen in DNAs placed in different chemical environments? a. X-ray diffraction d. isoelectric focussing b. SDS - polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis e. DEAE- cellulose chromatography c. spectrophotometry 29. The effect of ________ on eukaryotic cell membranes is to abolish transition temperature. a. phospholipids b. cholesterol c. gangliosides d. lipid-anchored proteins e. a and b 30. ___________ are specialized proteins that provide an environment in which proteins that have denatured can renature without interference. a. Foldases b. Chaperonins c. Molecular chaperones d. Ubiquitins e. b and c Biology 263 Cell Biology Joel Piperberg March 19, 2010 Second Exam Page # 4 Name ___________________________________ 31. Red blood cells with a surface area of _______ are lysed and the lipids of their membranes are totally extracted. These lipids are then spread over the surface of a water tank and the surface area covered is found to be 450 µ2. a. 90 µ2 b. 45 µ2 c. 150 µ2 d. 225 µ2 e. 900 µ2 32. Artificial membranes ______________. a. do not reseal spontaneously if pierced b. possess many properties in common with natural membranes c. lack some properties that natural membranes have d. b and c e. a, b and c 33. Which of the following membrane components is amphipathic at least to a small degree? a. cholesterol b. gangliosides c. transmembrane proteins d. phospholipids e. all of the above 34. Which of the properties below favor the passage of a molecule through a cell membrane? a. large MW b. hydrophobic c. b and d d. high negative charge e. hydrophilic 35. Which of the following molecules would pass least easily through a lipid bilayer? a. water b. carbon dioxide c. oxygen d. sodium chloride e. a, b and c 36. Which one of the following molecules will elute last from a gel filtration column? (Assume that all amino acids have the same molecular weight.) a. a globular protein composed of 187 amino acids d. a globular protein with 165 amino acids b. a very low molecular weight dye e. a protein consisting of 120 amino acids c. a cigar-shaped protein of 188 amino acids 37. Which of the techniques below might be used to effect a rapid purification and would be based on the solubility of the molecule to be purified? a. sucrose density centrifugation d. selective precipitation b. sodium hydroxide precipitation e. c and d c. ammonium sulfate precipitation 38. Which technique below is best for determining the precise quantity of radioactive isotope located in a specimen? a. c and d c. liquid scintillation counting e. ultracentrifugation b. atomic force microscopy d. autoradiography 39. Which technique below depends on the ability of a protein like a hormone receptor to bind to a specific molecule like the hormone it normally binds? a. DEAE-cellulose chromatography c. gel filtration e. homogenization b. selective precipitation d. affinity chromatography 40. One of the most striking features of membranes is exhibited by the distribution of membrane polysaccharides. This property is called __________. a. asymmetry b. diffusion c. exocytosis d. asynchrony e. effilosis 41. Which technique combines the effects of isoelectric focusing and SDS-PAGE to purify proteins? a. ion exchange chromatography d. autoradiography b. three-dimensional gel electrophoresis e. two-dimensional gel electrophoresis c. spectrophotometry Biology 263 Cell Biology Joel Piperberg March 19, 2010 Second Exam Page # 5 Name ___________________________________ 42. The -pleated sheet is stabilized by ________________. a. H bonds between polar amino acid R groups b. covalent bonds c. H bonds between amide (peptide) linkages oriented parallel to the molecule's axis d. acidobasic combinations e. H bonds between amide linkages, oriented perpendicular to the molecule's axis 43. A protein that can be washed off of a cellular membrane by a moderate concentration of a salt solution is called a(n) ______ protein. a. transmembrane b. lipid-anchored c. a and b d. peripheral e. b and d 44. During the summer, some organisms adjust the fluidity of their membranes by __________. a. increasing phospholipid tail length d. decreasing phospholipid tail length b. increasing tail unsaturation e. increasing tail saturation c. a and e 45. What is the minimum number of consecutive helix-forming and/or helix-indifferent amino acids required to form an -helix? a. 10 b. 14 c. 3 d. 7 e. 24.5 46. What bonds may be involved in holding together tertiary structure in proteins? a. peptide bonds b. ionic bonds c. H bonds d. disulfide linkages e. b, c and d 47. What is the highest level of structure exhibited by a protein consisting of one subunit? a. primary b. secondary c. tertiary d. quaternary e. pentary 48. What property of a pleated sheet region of a protein derives from the extended arrangement of its backbone? a. strength b. flexibility c. extensibility d. a and b e. hardness H CH2 CH2 CH2 N arginine C NH2 CH NH CH 3 CH 2 CH leucine CH O CH 2 aspartate CH2 SH cysteine C O HO CH OH tyrosine CH 3 CH valine CH alanine CH CH S CH 2 methionine O CH2 CH2 C NH2 glutamine 2 2 CH 2 CH OH 2 serine C OH O CH 2 CH 2 CH H 3 H C CH 2 glutamate 3 CH3 H glycine 2 phenylalanine 3 CH3 OH threonine 2 CH 2 NH lysine C CH 2 CH3 CH3 isoleucine CH2 CH 2 2 CH C 2 NH2 asparagine CH 2 histidine N proline H NH HN + C H CH2 HC CH C CH 2 tryptophan C HC N H II. Short Answer. Please be as brief as possible. 1. What is the highest level of structure exhibited by a protein having more than one subunit? (1 point) 2. If you are attempting to isolate mitochondria from liver tissue, what is the first step in the procedure? (1 point) Biology 263 Cell Biology Joel Piperberg March 19, 2010 Second Exam Page # 6 Name ___________________________________ Before starting this procedure, why would you place the liver tissue in a cold, isotonic solution? (2 points) BONUS QUESTIONS - SHORT ANSWER 1. JEOPARDY BONUS QUESTION (Your answer must be in the form of a question.) Subsequent answers need not be in the form of a question. (1 point) This "giant" ocean dweller has the largest eyes of any creature. 2. Draw a generalized tetrapeptide at physiological pH (pH 7.4). (3 points) 3. A protein has three globular regions, one that binds a specific ligand, one that binds to specific regions of DNA and one that unwinds the DNA double helix. These globular regions are connected by flexible hingelike regions. What are the globular regions of this protein called? (1 point) 4. In what purification technique does trichloroacetic acid (TCA) play a prominent role? (1 point) 5. What do you call a vesicle that is covered by a lipid bilayer and is used to deliver a drug or drugs to a specific target for chemotherapy of diseases like cancer? It is directed to the appropriate site by the placement of specific antibodies in the bilayer. (1 point) 6. What property determines the speed by which a protein or lipid can diffuse laterally through a membrane? (1 point) 7. Briefly name and define the levels of structure in proteins. What types of bonds are instrumental in holding each level of structure together? (8 points) Level of Structure Definition Bond(s) Involved Biology 263 Joel Piperberg Second Exam Name ___________________________________ Cell Biology March 19, 2010 Page # 7 8. Identify the techniques described below? (3 points) a. separation of proteins on the basis of molecular charge and molecular weight b. separation of proteins on the basis of their charge alone c. accurate determination of the position of radioactive molecules taken up by cultured cells 9. How is charge eliminated as a factor in the separation of proteins by SDS-PAGE? (1 point) 10. Name one difference found between different membranes that contributed to the downfall of the Unit Membrane model of membrane structure. (1 pointed) 11. What is the name of the uncommon process whereby a membrane lipid moves from one leaflet of the membrane to the other leaflet? This movement can sometimes be reversed by the action of an enzyme. (1 point) Biology 263 Cell Biology Joel Piperberg March 19, 2010 Second Exam Page # 8 Name ___________________________________ 12. You fuse a human and a mouse cell together and then label the resultant cell with fluorescently labeled antibodies against human and mouse membrane proteins. The anti-mouse antibodies are labeled with fluorescein (green) and the anti-human antibodies are labeled with rhodamine (red). Based on its appearance, what is the cell called immediately after fusion? (1 point) What do you call a cell that results from the fusion of two different cell types like a mouse cell fusing with an alligator cell? (1 point) 13. You are designing a drug that must pass through a liver cell membrane easily to cure a particular liver ailment. What two properties must that molecule have in order for it to pass easily through the membrane? (2 points) 14. Scientists have sequenced proteins by using specific proteases to "clip" a purified protein preparation between two specific amino acids thus forming a number of moderately sized fragments; they have used acid hydrolysis to produce smaller fragments. Each fragment can then be sequenced by breaking the moderate fragments into dipeptides, which are easily sequenced. The fragments below are obtained after the initial enzymatic cleavages. Can you deduce the sequence of the original polypeptide? (HINT: the original cleavages at specific locations differ depending on which proteolytic enzyme was used to create each fragment; this causes an overlap in the fragments' sequences.) (2 points) (Use the back of the test if you need to) N - phe - val - asp - gly - ala - leu - tyr - arg - C N - ala - tyr - arg - phe - gluN - aspN - leu - C N - leu - tyr - arg - tyr - gluN - ser - gly - cys - C N - ala - ala - tyr - arg - C N - gluN - aspN - leu - val - ala - phe - val - asp – C 15. Look at the following experimental results obtained by a deep-space probe investigating life on other planets. Membrane proteins were extracted with SDS and subjected to SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on tube gels. The resultant gels were stained with Coomassie Blue, which stains proteins (a) and Periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS) stain, which specifically stains carbohydrates (b). When whole cells or inside-out vesicles were exposed to lactoperoxidase and 125I, the profile in Graph (c) was obtained when the gels were cut into 1 mm thick slices and the radioactivity was monitored in Biology 263 Cell Biology Joel Piperberg March 19, 2010 Second Exam Page # 9 Name ___________________________________ the scintillation counter. In Graph (d), we see the results of exposure to galactose oxidase and 3H borohydride, a process, which radioactively labels sugar residues to which galactose oxidase and 3H borohydride are exposed. In Graphs (c ) and (d), the solid line indicates labeling of whole cells and the dotted line indicates labeling of inside-out vesicles. What kind of membrane proteins are A, B, C and D? (i. e., On which surface are they exposed? Do they have polysaccharides and on which side of the membrane are the polysaccharides exposed, if present?) Ignore any preconceived notions about membrane proteins! Just interpret the data!!! (Please see the following page for the graphs.) Protein Is it exposed on the intracellular or Is it a glycoprotein? extracellular surface? Which leaflet has the sugar groups (if any)? A B C D Which protein, if any, may be involved in membrane transport? (4 points) Which protein has the highest molecular weight? (1 point) Biology 263 Joel Piperberg Second Exam Name ___________________________________ Cell Biology March 19, 2010 Page # 10