* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHAPTER 14: Genes in Action Essential Ideas
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
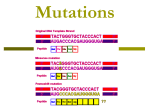
CHAPTER 14: Genes in Action Essential Ideas-VOCABULARY Gene-a segment of DNA whose nucleotide sequence codes for a protein. Mutation - Changes in the nucleotide sequence of a gene’s DNA Mutagens cause mutations, include environmental factors ike chemicals, X-rays, and UV light Genetic Mutations – single or small changes to individual genes DNA sequence Point mutations include; silent, missense and nonsense SILENT mutation - the change in the codon results in the same amino acid- UAU UAC both code for tyrosine NONSENSE mutation - a codon is changed to a stop codon; protein may be too short to function -UAC UAG (a stop codon) MISSENSE mutation - involves the substitution of a different amino acid, Frameshift mutations may be caused by additions or deletions, they create missense or nonsense mRNA Genetic Diseases ( aka genetic disorders) like: CF, Duchennes MD, ColorBlindness are caused by point or frameshift mutations Sickle Cell Anemia: MISSENSE MUTANT -Defective Hemoglobin Gene-You can’t carry oxygen well Cystic Fibrosis: DELETION MUTANT -Defective Protein is made that creates excess mucus; clogs lungs. Color Blindness: SEX LINKED - Inablity to distinguish colors (8% of male population) Hemophilia: SEX LINKED - Inablity of blood to clot Muscular Dystrophy: SEX LINKED -Loss of muscle that begins in early childhood Chromosomal Mutations. Large scale change in the gene sequence including deletion, duplication, inversion, translocation Tetrad formation in Prophase I of Meiosis- when Chromosomal changes occur Chromosomal or Genetic Syndromes – caused by chromosomal mutations, include; Williams, Alagille, or Downs Chromosomal Deletion : Chromosome loses a segment, ex. Williams Syndrome- Chromosome 7 loses an end piece Chromosomal Duplication: chromosome segment being REPEATED in the same chromosome, ex inv Dup 15 syndrome Chromosome Translocation: exchange of chromosomal segments between two, NON-HOMOLOGOUS chromosomes. ex.Alagille Syndrome Chromosome Inversion- a segment of a chromosome being turned 180 degrees. Williams Syndrome- Children have a pixie look Poor academic skills, good verbal and musical abilities-Chromosomal Deletion inv Dup 15 syndrome- Poor muscle tone, mental retardation, seizures, curved spine, and autistic characteristics, Chromosomal Duplication Alagille Syndrome- Distinctive face, abnormalities of eyes & internal organs, and severe itching. Translocation Saethre-Chotzen syndrome- Chromosome Inversion Polyploidy when extra chromosomes are found in an individual, for example trisomy 21 or Downs syndrome Non disjunction event during Anaphase of Meiosis in which chromosomes fail to separate that can lead to polyploidy DOWNS SYNDROME =TRISOMY21 (3 copies of a chromosome 21) mental delays, changes in blood vessels and connective tissue DNA Technology - Genetic Engineering – the use of technology to understand and change gene function The Human Genome Project Decoded an entire length of DNA in 2003 Genetic Sequencing – decoded nucleotide sequence for the 23,000+ human genes, allows for the detection and treatment of genetic disease and cancer. Gene Therapy -good copies of a gene are introduced into those individuals affected by genetic disease, often using viruses Virus – a non-living vector that infects cells with DNA and uses the cells machinery to reproduce toil the cell lyses or explodes