* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Cycle regulation
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
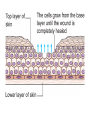
Cell Cycle Regulation Observations of Cells • A. Cells typically grow until their cell membranes (or cell walls) come into contact with another structure. • 1. Cells grown in a lab grow until they touch the edge of the petri plate or another cell. • 2. When you cut your skin or break a bone, the cells at the site of the injury will grow until they fill in the empty space. • **These two examples show that there are controls on when cell division occurs. Controls on the Cell Cycle • External Regulators- proteins that respond to events outside of the cell • 1. Hormones (Growth factors) are an example. • a. When an organism is supposed to grow bigger, it may release growth hormone that causes certain cells to respond by progressing through the cell cycle. • 2. Cells touching each other or their surroundings is another example. • a. Cells will stop growing and dividing when they contact each other or an object in their surroundings Other Controls on the Cell Cycle • A. Internal Regulators- proteins that respond to events that occur inside the cell. • 1. One example is a protein that will not allow the cell to enter mitosis until all the DNA has been replicated • 2. Another example is a protein that prevents anaphase from occurring until all the chromosomes have attached to a spindle.