* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download RNA interference was popularized by work in C
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
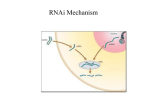
RNA interference was popularized by work in C.elegans. When long double-stranded RNAs were injected into a worm’s gonad, a standard way of introducing transgenes into worms, they blocked the expression of endogenous genes in the sequence specific manner. In eukaryotes, most protein coding genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II, which generates pre-mRNAs that then process to form mature mRNAs. These mRNAs are then transported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, where they are translated. RNAi can regulate endogenous gene expression. RNAi can be set in motion by genomically encoded short regulatory RNAs known as microRNAs. In algae, worms and flies, RNAi can be activated by endogenous transposition. In plants and cultured insect cells, RNAi also has a role in antiviral defense, in which viral double-stranded 1 RNAs are targeted for destruction by the RNAi machinery. When long double-stranded RNAs enter a cell, they are recognized and cleaved by Dicer, which is a member of the RNaseIII family of double-stranded RNA specific endonucleases. Cleavage by Dicer creates short double-stranded RNAs that are characterized by two-nucleotide long 3’ overhangs. These are called small interfering or siRNAs. siRNAs can form a ribonucleoprotein complex called RISC, or RNAi Silencing Complex. This complex includes “Slicer”, an Argonaute protein with a RNAse H-like domain called PIWI.( Argonaute Is the signature component of RISC) RISC first mediates the unwinding of siRNA duplex. A single-stranded siRNA that is coupled to RISC. Then binds to target mRNA in the sequence specific manner. The binding mediates target mRNA 2 cleavage by slicer. The site of cleavage falls in the middle of the region of siRNA complementarity. The cleaved mRNA can be recognized by the cell as being aberrant and then destroyed. This prevents translation from occurring, silencing the expression of the gene from which the mRNA was transcribed. In plants, the aberrant RNA resulted from RISC mediated cleavage can also serve as a template for RNA dependent RNA polymerase, or RDRP. This process relies on unprimed RNA synthesis, in which the aberrant RNA is used as a template. The resulting double-strand RNA IS a substrate for DICER activity, which generate more siRNAs. In some organisms with endogenous RNAi mechanisms, for example, fungi, plants worms and mammals, RNAi also involve another amplification step. In this step, single-stranded siRNAs not associated with RISC bind to their target 3 RNAs in the sequence specific way, and serve as a primer for RDRP to polymerize the antisense RNA strand, such specificity is intrinsically sensitive to natural sequence variation. The double-stranded RNA molecule that is created serves as a substrate for DICER, which cuts it into siRNAs. In turn this can either unwind and prime RNA dependent RNA polymerization, or together with RISC, mediate the cleavage of target mRNAs. This amplification, coupled with RNAi spreading between cells, is thought to underlie germline transmission of RNAi in worms. RNAi spreading has also been described in plants, but not in mammals. 4