* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Answers to Biological Inquiry Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Hedgehog signaling pathway wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
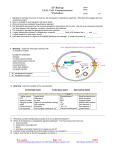
Answers to Biological Inquiry Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site Chapter 52 Figure 52.14 BIOLOGICAL INQUIRY QUESTION: How might it be possible for a single molecule to exert different effects on cells at different concentrations? ANSWER: Different concentrations of a signaling protein can exert different effects on cells when, for example, different cells express different isoforms of a plasma membrane receptor for the protein. If one cell expresses a high-affinity receptor and another cell a low-affinity receptor, the two cells would respond to the signaling protein at different concentrations. Likewise, the different receptors may be linked with different second messenger molecules generated within the cell. These messengers, such as cAMP and Ca2+, may have different effects on cell function. Figure 52.17 BIOLOGICAL INQUIRY QUESTION: Are there other examples in animals in which one protein binds another to prevent its action? ANSWER: Yes, and such activity occurs not only during development but at all stages of life. For example, certain proteins secreted into the blood of adult mammals can bind signaling proteins such as hormones, thereby sequestering them and preventing their actions.