* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Communication
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
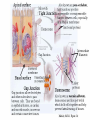
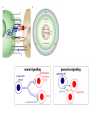
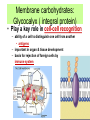
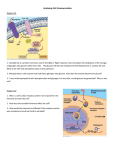
Cell Communication Ch. 11 How are signals sent locally? • Cell Junctions: Animals and Plants pass molecules through the plasma membrane. • Cell-cell Recognition: Receptor sites on animal cells protrude from its surface and attach. – Composed of the glycocalyx. Also responsible for contact inhibition. • Paracrine Signaling: Local regulatory molecules are sent to neighboring target cells. • Synaptic signaling: neurotransmitters across the synapse. Membrane carbohydrates: Glycocalyx ( integral protein) • Play a key role in cell-cell recognition – ability of a cell to distinguish one cell from another • antigens – important in organ & tissue development – basis for rejection of foreign cells by immune system How are signals sent long distances? • Hormone Signaling: Endocrine systems sends signals through body fluids, often through the blood. – target cell : any cell that has a specific receptor for an antigen or antibody or hormone or drug, or is the focus of contact by a virus or phagocyte or nerve fiber etc. The Signal Transduction Pathway • Small number of extracellular signal molecules produce a major cellular response. Sutherland’s epinephrine STP • Three stages: – Reception: The protein binds to a cells surface receptor. This protein is often called a ligand. – Transduction: Signal molecule changes the receptor protein, the change is relayed to a secondary messenger. – Response: Secondary messenger induces the cellular response. G Protein Point of the two pathways? • Sutherlands Epinephrine pathway: epinephrine does not directly break down glycogen for fuel reserve. It does this through intermediate steps. • G Protein receptors – Used in yeast for mating, by hormones such as epinephrine, neurotransmitters, vision and smell. – G protein when active picks up GTP sends it to an enzyme and causes conformational shape which allows for the cellular response. – Botulism, cholera, pertussis (whooping cough) intefeer with the G-Protein funcion. – 60% of all medicines used today influce the G- protein pathway.