* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Communication Part I
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
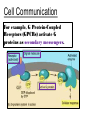
Warm-Up (12/07) On the piece of white paper from the back, answer the following question. No Warm-Up! Get working on your test! You have 20 minutes exactly! Name Date Period Cell Communication Cells communicate using signals (aka ligands) Ligand binds receptor at surface of cell Receptor changes shape, activating second messengers Second messengers change cell activities and/or affect gene expression Cell Communication Signal transduction: when a ligand causes a cellular response genes to be expressed http://www.wiley.com/legacy/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/signal_transduction/signal_transduction.htm Cell Communication Like an enzyme to a substrate, a receptor only recognizes a specific ligand ligand receptor before after Cell Communication For example, G Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCRs) activate G proteins as secondary messengers. Cell Communication Signaling cascades are chains of secondary messengers. Each one activates the next by modifying it: for example, phosphorylation (putting on a phosphate). Cell Communication Usually, the ultimate goal is turning on and/or off genes. For example, ethylene ripens fruit. nucleus P unactivated receptor 2nd messenger enzyme genes activated ethylene (ligand) P receptor 2nd messenger enzyme genes Critical Thinking Question #1 Discuss this question with your partner and write or represent it. I will call on three people to share their partners’ answers. Describe the molecular nature of a chemical signal and explain the key elements of a signal transduction pathway responsible for causing a cellular response. How do concentration levels of signal affect the cellular response? Closure On the piece of white paper from the back, answer the following question: Explain how a specific cellular signal can promote production of a specific protein. Name Date Period Scale 1 – 10