* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 8 Basics: Organelles Overview: Types of signaling Types of
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
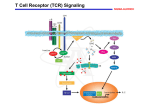
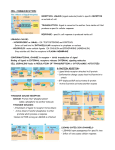
Lecture 8 Basics: Organelles Overview: Types of signaling 1. Intracellular Definition: Examples: 2. Cell-cell recognition Definition Examples: 3. Local signaling Definition: Paracrine Synaptic Types of receptors 4. Hormone Signaling: Definition: Examples: Three steps to signaling: Four Receptor Types G protein-coupled receptor Example: Steps in receptor response: (summarize figure legend in your own words) 1. 2. 3. 4. Receptor Tyrosine Kinase: Kinase definition: Difference from G protein-coupled receptor: Example: Steps in response: 1. 2. 3. 4. Ligand gated ion channels Action: Example: Steps in response: 1. 2. 3. Intracellular receptors Found: Common ligands: Location of action: Steps in response: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Class Notes Summary table: Signaling types: Signaling type Short or long distance Signal enters cell? Example Binding of a ligand to a ligand gated ion channel: A. Causes a conformational change in the protein B. Allows ions to flow across the membrane against their concentration gradients C. Causes the movement of a G-protein D. Results in the hydrolysis of ATP E. Both A and B Example: G protein-coupled receptor and cholera toxin Normal digestion: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Regulatory hormone binds to a g protein-coupled receptor Changes the shape of the receptor, alpha unit releases GDP and binds GTP Active alpha activates adenylyl cyclase, which produces cyclic AMP cAMP activates protein kinase A (PKA) to add a phosphate to CFTR channel Channel opens, chloride exits, water follows, extra fluid aids breaking down of food 6. Bound GTP on alpha subunit of g protein breaks off phosphate, becomes inactive very quickly 7. Fluid secretion stops Cholera Toxin 1. Cholera toxin binds to a glycolipid and injects a protein into the cell 2. The toxin forces a molecule to bind to the alpha subunit that blocks the GTP in place