* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download RNA - GVI.cz
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
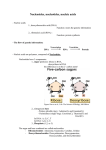
MOLECULAR GENETICS - RNA Výukový materiál GE 02 - 46 Tvůrce: Mgr. Šárka Vopěnková Tvůrce anglické verze: ThMgr. Jiří Foller Projekt: S anglickým jazykem do dalších předmětů Registrační číslo: CZ.1.07/1.1.36/03.0005 Tento projekt je spolufinancován ESF a SR ČR 2014 RNA a necessary component of protein synthesis (= synthesis of proteins) synthesis of proteins = protein synthesis : fundamental process, by which the information from DNA is transferred into a particular sign polynucleotide chain RNA three types of RNA: 1) m RNA messenger mediator linear synthesis in the cell nucleus enzyme RNA – polymerase the triplet of nucleotides after each other following on mRNA is called codon RNA the nitrogen base is bound on the ribosome carbon in position1, different from DNA because of the occurance of uracil instead of thymine remaining bases (adenine, cytosine, guanine) are identical on both nucleic acids RNA RNA very various: mono helix and linear molecules also double helix structures > t RNA 3 types of RNA: m RNA t RNA r RNA RNA 1) m RNA messenger mediator information it develops by the transcription from DNA (enzyme RNA – polymerase) hundreds to thousands of nucleotides linear synthesis of m RNA in the cell nucleus a triplet of nucleotides following behind each other placed on mRNA is called codon RNA 2) t RNA transfer complicated structure short – 74 až 95 nucleotides the cord creates 4 arms secondary structure - it reminds a shamrock trefoil RNA particular arms attach to each other => they make up a more complex space formation – so called tertiary structure RNA AMA bind on the acceptor arm anticodon arm it contains a triplet of nucleotides = anticodon each anticodon in tRNA is complementary to the particular triplet of nucleotides in mRNA – to the codon RNA 3) rRNA ribosomal contained in ribosomes translation proceeds on ribosomes genetic information transcribed from DNA into mRNA determines the order of amino acids in the protein chain DESCRIBE THE PICTURE REVISION Which picture depicts the tertiary structure of tRNA ? SOURCES KOČÁREK, Eduard. Genetika: obecná genetika a cytogenetika, molekulární biologie, biotechnologie, genomika. 2. vyd. Praha: Scientia, 2008, 211 s. ISBN 978-80-8696036-4.